Web applications are no longer just delivery channels. They are the core systems through which products scale, users engage, and operations automate. Tools such as Slack, Trello, or Notion that were initially developed as simple web applications designed to address a particular issue are now transforming the way teams work and innovate.
A web application is a dynamic platform that combines the fluidity of websites and the functionality of software. Web applications can be accessed on devices and browsers, which allows users to execute advanced tasks without downloading any application. For founders and decision-makers, understanding what goes into creating one will help you make smarter decisions about time, technology, and investment.
This guide will take you through a step-by-step process, from idea to launch, explaining everything you need to know to transform your vision into a full-scale web application that is ready to enter the market.
What Is a Web App and How It Works
Before discussing how to develop a web app, it helps to understand what distinguishes a web application from other software models.
A web application is a server-driven software system accessed through a browser. Core logic, data processing, and updates are handled centrally, allowing teams to deploy changes quickly without requiring user installations or manual updates. This centralized model enables rapid iteration, consistent behavior, and easier scaling.
Most web applications are built from three core components:
-
Frontend (Client-Side)
The interface users see and interact with. Built using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript frameworks such as React, Angular, or Vue, the frontend handles layout, interactions, and client-side logic.
-
Backend (Server-Side)
The system that manages business logic, authentication, permissions, and data processing. Common backend technologies include Node.js, Python (Django or Flask), and Ruby on Rails.
- Database
The persistent storage layer where application data is stored and retrieved. Popular options include PostgreSQL, MongoDB, and MySQL.
Web apps may also be classified as:
-
Static Web Apps: Simple, content-driven site with little to no interactivity.
-
Dynamic Web Apps: Data-driven platforms that respond to what users input.
-
Single-Page Applications (SPAs): Applications that update without loading a page multiple times.
-
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs): Hybrid applications that merge web and mobile apps. It is the best place to start when you are considering how to develop a progressive web app.
The Step-by-Step Process: How to Develop a Web App from Scratch
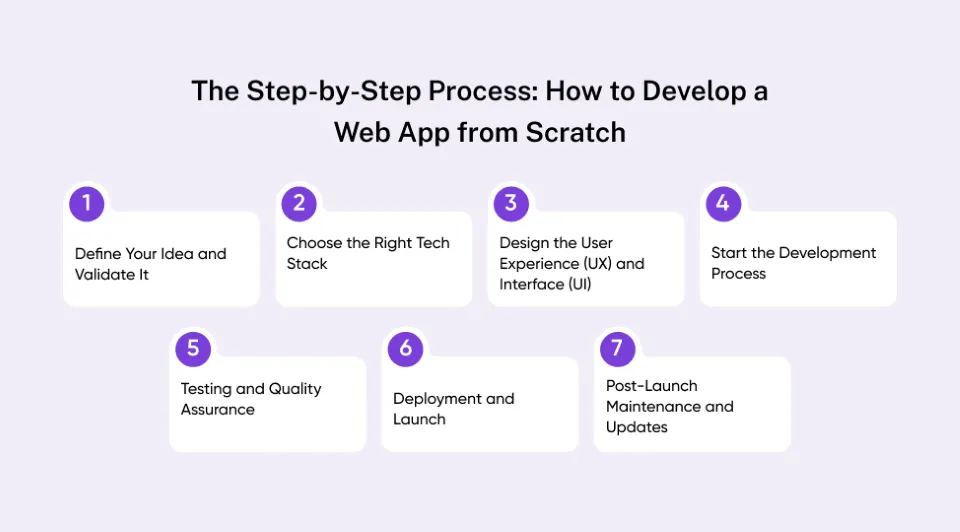
Step 1: Define Your Idea and Validate It
The first step in how to develop a web app is to have a clear idea and ensure that the idea addresses a real problem. Skipping validation usually surfaces later as wasted development time, rework, and misaligned features. An idea that is proven to be valid lays out the foundation for all that is to follow.
Here is how to strategically approach it:
-
Determine the Main Issue: Start by asking yourself, “What issue is my web app solving? Is it about efficiency, connecting people, or making a complicated process easier?”
-
Identify Your Target Audience: Narrow down your target users. Note their needs, behaviors, and pain points.
-
Study the Market:
Do a competitor analysis to identify gaps or opportunities.
Check user reviews and product forums to find out what available solutions lack.
-
Create an MVP (Minimum Viable Product): Rather than creating the entire application, you should begin with an MVP. It is used to validate assumptions at the lowest cost.
-
Obtain Feedback Early: Conduct surveys or interviews to confirm demand before investing all resources.
Step 2: Choose the Right Tech Stack
Your tech stack is not about trends. It is about how fast you need to move now, and how far you expect the product to scale later.
Selecting the right technology stack is crucial when learning how to develop a web app. The tech stack defines the performance, scalability, and flexibility of your web app, along with the speed at which it will be developed. It is the main factor when the question “how long does it take to develop a web app?” comes to your mind
A web application stack consists of three layers:
Frontend (Client-Side):
Visual interface that the user interacts with. Popular choices include:
-
React.js: For scalable and dynamic single-page applications.
-
Vue.js: Lightweight and suitable for quick development.
-
Angular: A systematic framework that can be used to develop enterprise-level applications.
Backend (Server-Side):
It is concerned with business logic, database interactions, and server communication. The typical technologies used for the backend are:
-
Node.js: fast and ideal for real-time applications.
-
Python (Django or Flask): rapid development and high security.
-
Ruby on Rails: A great fit for startups that create MVPs in a hurry.
Database and Infrastructure:
-
Databases: PostgreSQL, MongoDB, MySQL.
-
Hosting: AWS, Google Cloud, Azure.
When picking your stack, remember:
-
Scalability and complexity of a project.
-
Availability and skill sets of developers.
-
Integration requirements (APIs, payment gateways, analytics tools).
Step 3: Design the User Experience (UX) and Interface (UI)
Most web apps fail not because of missing features, but because users cannot immediately understand what to do.
Design is where your idea begins to have a physical form. A good UX and UI can be the key factor between an app that users will fall in love with and an app that users will leave as soon as they visit.
This is how you should approach it:
-
Begin with User Flows: Visualize user navigation in your app, from sign-up to the main task. This makes sure that your design is useful in reality.
-
Design Wireframes and Prototypes: Figma, Adobe XD, and Sketch are useful tools that allow you to see the layout, interactions, and hierarchy of content before the development process starts.
-
Value Simplicity and Consistency: Have clean interfaces that are easy to use. Each button, color, and icon must be purposeful.
-
Pay Attention to Accessibility: Use best practices such as readable fonts, contrast proportions, and keyboard navigation to be inclusive.
-
Design to be Responsive: Your web application has to be compatible with desktops, tablets, and mobiles.
Step 4: Start the Development Process
It is now time to build what you have conceptualized, designed, and stacked together. This is where architectural decisions turn into real constraints—good or bad—that will shape your product long-term.
An effective development process normally includes the following stages:
Turn your layout into responsive designs with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript frameworks.
Prioritize performance. Optimize images, decrease loading time, and maintain similarity in UI between browsers.
Develop APIs, authentication systems, and data processing logic.
Use RESTful or GraphQL APIs to have proper frontend-backend communication.
Connect your backend with a database (e.g., PostgreSQL, MongoDB) to enable storing and retrieving data in real-time.
- Agile & Iterative Approach:
Split development down into sprints. Periodically review and refine them using feedback.
Make sure records are updated to allow transparency between teams.
Step 5: Testing and Quality Assurance
Teams that postpone testing until “after development” almost always ship instability into production.
When the first version of your application is ready, it is time to make sure that it works perfectly. Testing and QA are critical components of web app development because they detect bugs, increase stability, and improve user experience before release.
A proper QA procedure has several levels of testing:
Tests every feature, from login forms to payment gateways, to ensure that it functions as expected.
Includes actual users to test the interface to make it user-friendly and easy to use.
Stress tests your web application with JMeter or LoadRunner with large data loads or a lot of traffic.
Detects vulnerabilities like SQL injections or weak flows of authentication that might compromise user data.
- Cross-Browser and Device Testing:
Ensures your app works similarly across all browsers, like Chrome, Safari, Firefox, etc.
Regression can be detected early by using automated testing frameworks such as Selenium, Cypress, and Playwright to speed up the process.
💡Suggested Read: AI Security in Web Application Firewall
Step 6: Deployment and Launch
After a considerable amount of testing, your web app will be ready to go live. However, successful deployment does not come by simply launching. It is instead a well-thought-out procedure that guarantees performance, security, and reliability.
The following are some tips on how to handle deployment:
- Choose a Hosting Platform:
Use trusted solutions such as AWS, Google Cloud, Azure, or Vercel, depending on the requirements of scaling and cost.
- Establish Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD):
Streamline updates with automated testing and deployment pipelines, such as GitHub Actions or Jenkins.
- Set up the Production Environment:
Make sure that there are proper environment variables, SSL certificates, and domain settings.
- Measure Performance and Stability:
Monitoring tools such as New Relic or Datadog can be used to track real-time load times, errors, and uptime.
- Run a Pre-Launch Checklist:
-
Check that everything works as desired.
-
Ensure responsiveness across all devices.
-
Make sure that analytics and backups are set up.
Step 7: Post-Launch Maintenance and Updates
Post-launch maintenance is an ongoing procedure that makes sure your app remains safe, effective, and relevant. This step usually either makes or breaks the difference between a static product and a scalable business asset in the long term.
Monitor uptime, response time, and error logs with tools such as Google Analytics, Sentry, or New Relic.
Encourage early adopters to share their experiences in surveys or in-app notifications. Their response can be used to guide feature prioritization.
- Roll Out Regular Updates:
Fix bugs, improve functionality, and add web application features to make the product competitive and fresh.
- Ensure Security and Compliance:
Keep dependencies updated, conduct frequent security audits, and comply with data protection regulations such as GDPR.
- Gradually Scale Infrastructure:
If you need to scale to larger user bases, you should optimize servers, databases, and APIs without affecting performance.

Cost Breakdown: How Much Does It Cost to Develop a Web App?
Perhaps one of the most frequently asked questions that founders consider before starting is: how much does it cost to develop a web app? The solution varies based on several factors, which include complexity, features, technology stack, and the team that you will hire.
Faster timelines and lower upfront costs often trade directly against scalability, performance, and long-term stability.
A brief overview of common cost elements:
| Cost Factor |
Description |
Estimated Range |
| App Complexity |
MVP with essential features; mid-level apps with integrations; enterprise-grade with analytics, automation, and scalability. |
$15,000 to $150,000+ |
| UI/UX Design |
Custom user interface, wireframing, and user testing to ensure a seamless experience. |
15 to 25% of the total cost |
| Technology Stack |
Depends on the frontend (React, Angular, Vue) and backend (Node.js, Django, Laravel) frameworks used. |
Varies based on tools and licenses |
| Development Team |
In-house: higher cost, more control. Outsourcing: lower cost, access to diverse talent. |
$30 to $150/hour, depending on region |
| Maintenance & Hosting |
Continuous support, hosting, server scaling, and feature updates post-launch. |
15 to 20% annually of the initial cost |
Collaborating with a web app development services provider can help you determine these variables correctly and make your investment align with long-term purposes.
Timeline: How Long Does It Take to Develop a Web App?
Understanding how long does it take to develop a web app will allow founders to make realistic expectations and plan funding, marketing, and recruitment accordingly. Timelines are usually based on the complexity of your app, design needs, and how you develop it.
Here is a rough estimate of how much time you will need:
| Development Stage |
Key Activities |
Approx. Duration |
| Discovery & Planning |
Requirement gathering, defining user personas, and selecting tech stack. |
2–4 weeks |
| UI/UX Design |
Wireframes, prototypes, and design validation. |
3–5 weeks |
| Development |
Frontend and backend coding, API integrations, and database setup. |
8–14 weeks |
| Testing & QA |
Performance, usability, and security testing. |
2–4 weeks |
| Deployment & Launch |
Hosting setup, CI/CD configuration, live deployment. |
1–2 weeks |
| Post-Launch Maintenance |
Continuous updates and monitoring. |
Ongoing |
Average timeline:
The simplest MVP can be developed in 1-2 months, while a more elaborate app would be developed in 6-9 months, or more, based on iteration cycles and feedback.
In practice, unclear requirements, delayed feedback, and late architectural changes are the most common reasons timelines extend.
Agile development is a popular choice for many startups to speed up timelines without compromising quality. They divide large projects into sprints that can be delivered quickly and tested in the early stages.
Future Trends: The Rise of Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) and What’s Next
Keeping an eye on future technology trends makes product choices future-proof and helps you prioritize the features you should build.
Key trends to watch:
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs):
PWAs are on the rise because they provide native performance, offline capabilities, and can be installed easily without the overhead of application stores. When considering cross-platform strategies, it becomes more important to learn how to develop a progressive web app to have the user adopt it quickly.
Serverless & Edge Computing:
Edge computing reduces latencies and makes scaling easier. Serverless models reduce operational costs and are capable of accelerating the time-to-market for startups.
AI-Powered Experiences:
Personalized user experience and automation of repetitive tasks are going to be the standards of integrated AI (recommendations, smart search, generative features).
API-First & Microservices:
Modular, API-driven design speeds up development, allows parallel work streams, and simplifies third-party integrations.
Greater Concerns about Privacy and Security:
With stricter regulations and user expectations, building secure, compliant systems from day one is non-negotiable.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Developing a Web App
Even with the most optimal strategy, most startups fail in the implementation process. Knowing these challenges when developing a web app helps you avoid expensive failures in the future.
1. Skipping Market Validation:
Building without validating your idea will result in the creation of products that no one wants. Test early with real users before committing to complete development.
2. Poor Scope Management:
Attempting to add all the features simultaneously may slow down the launch and increase the budget. Concentrate on building a good MVP.
3. Ignoring UI/UX Principles:
Even the most advanced backend cannot save a clunky interface. Focus on design, convenience, and easy navigation.
4. Lack of Testing:
Rushing to release without proper QA results in bugs, crashes, and poor user experience. Constant testing during development is important.
5. Neglecting Maintenance Planning:
Frequent updates, performance measurement, and user feedback cycles are the key to success in the long term.
Start Building Your Web App the Right Way
Learning how to develop a web app isn’t just about coding. It’s about turning an idea into a functional, scalable, and user-centric product. From ideation and design to development, testing, and maintenance, each phase plays a crucial role in ensuring your app’s long-term success.
You would get the best results when you:
Begin with a product vision and user objectives,
Invest in a skilled cross-functional development team, and
Stay agile and be willing to change with user feedback and market changes.
Regardless of whether you are creating a basic MVP or a full-scale enterprise platform, you need to know your users, validate continuously, and use modern technologies such as AI, serverless computing, and Progressive Web Apps to succeed.
Quokka Labs helps both startups and businesses realize their digital concepts with accuracy, imagination, and creativity. We change the way businesses develop and scale web applications.



 Facebook
Facebook
 Twitter
Twitter
 LinkedIn
LinkedIn
 Pinterest
Pinterest