You have the idea. You roughly know when you want to launch. But you still can’t get a straight answer on how much this React Native app will actually cost in 2026.
If you’re trying to plan a React Native app in 2026, the hardest part is not design or development. It’s budgeting. Mobile spending keeps growing every year, and a big chunk of digital budgets now go into mobile apps, not just websites. For a lot of startups and product teams, real-world app budgets sit anywhere between 20,000 and 200,000 USD, sometimes more, depending on complexity and markets.
This breakdown reflects real React Native projects built for startups and scaling teams in 2026. The numbers assume production-grade quality, App Store readiness, and real post-launch usage—not demo apps or throwaway MVPs.
The tricky part is this: react native app development cost is not one fixed number. It changes based on:
-
How big and complex your feature set is
-
What kind of design quality you want
-
The backend, APIs, and 3rd party tools you pick
-
Your team model and region
-
How serious you are about updates after launch
React Native often cuts total spend compared to building two separate native apps, but you still need a realistic range to plan around.
In this guide, we’ll walk through a complete breakdown of react native app cost in 2026 – from core cost components and pricing tiers to team choices, hidden costs, and a practical way to estimate your own budget.
Let’s start with the building blocks.
Core Components of React Native App Development Cost in 2026
When people ask “what’s the react native app development cost?”, what they’re really asking is: what are all the pieces I’m paying for?
At a high level, your budget usually splits into a few core buckets:
Discovery and planning
-
Workshops, requirement gathering, user stories, basic architecture
-
Makes the rest of the work clearer and reduces rework later
UX and UI design
-
Wireframes, clickable prototypes, visual design
-
Platform-aware layouts for iOS and Android
-
Design systems, components, and interaction patterns
Frontend (React Native) development
-
Building screens, navigation, and state management
-
Implementing features like login, feeds, search, checkout, etc.
Backend, APIs, and integrations
QA and testing across devices
-
Manual testing on different phones and OS versions
-
Automated tests where it makes sense
-
Fixing bugs and edge cases
Launch, monitoring, and ongoing improvements
-
App Store and Google Play prep
-
Crash reporting, analytics, performance monitoring
-
Post-launch fixes and small enhancements
Why 2026 is a bit different than earlier years
In 2026, a few things push react native development cost in a slightly new way:
-
User expectations around performance and polish are higher
-
Cross-platform tooling is mature, making React Native pricing more predictable
So, the components stay similar, but the quality bar and expectations are higher than a few years back.
Key Factors That Drive React Native App Development Cost
Once you know the cost buckets, the next step is to understand what actually makes numbers go up or down.
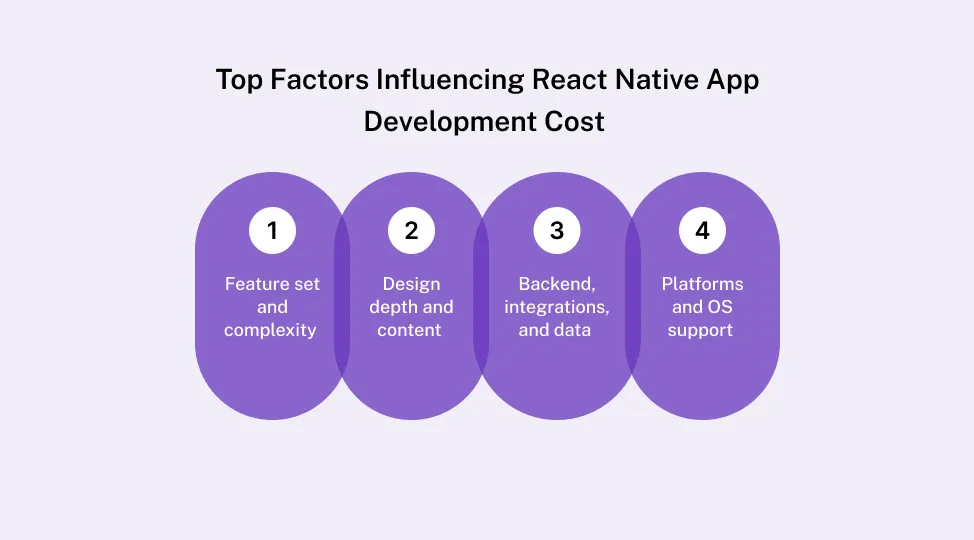
A. Feature set and complexity
This is usually the biggest driver of cost of react native app.
Simple apps
Medium complexity apps
-
10–20 screens
-
Payments and subscriptions
-
Push notifications
-
Basic chat, maps, or search
-
Some offline behavior
Complex apps
-
Role-based access and multi-tenant setups
-
Real-time features (live updates, chats, dashboards)
-
Heavy offline sync and conflict handling
-
Multiple 3rd-party integrations and custom back office tools
Every climb in complexity usually means: more design, more frontend logic, more backend work, more testing. That’s how react native app cost grows in a very predictable way.
B. Design depth and user experience
You can go light or deep on design, and it changes react native development cost a lot.
Basic design
Advanced design
-
Fully custom branded UI
-
Rich animations, transitions, micro-interactions
-
Special layouts for tablets and foldables
More design work = more front-end work. But in many cases, good UX also improves ROI, so it’s not just extra spending, it’s an investment.
C. Backend and 3rd-party integrations
Even the best React Native frontend needs data and services:
-
Custom backend vs BaaS (Firebase, Supabase, etc.)
-
Payment gateways, analytics tools, SMS and email providers
-
CRMs, internal systems, or ERP integrations
The more services you connect, the higher the cost to build a react native app. Each integration has its own quirks, testing, and edge cases.
D. Platforms, devices, and OS versions
React Native helps you target both iOS and Android from one main codebase. Still:
-
Supporting older OS versions can add effort
-
Tablets and different form factors need layout attention
-
Device fragmentation especially on Android means more QA
All of this rolls into the final react native app development cost for your project.
Once you know what drives cost, the obvious next question is: how much does it all add up to in real numbers?
💡Suggested Read: React Native Cross-Platform Development: Best Strategies and Tips
Pricing Tiers – React Native App Cost Ranges for 2026
Let’s look at some practical tiers to understand react native pricing in 2026. These are not strict quotes but useful ranges to think with.
A. Simple MVP – starter React Native app
Typical features:
Timeline:
- Roughly 8–10 weeks with a small, focused team
Estimated react native app cost range:
- Around 15,000 – 40,000 USD, depending on region and team structure
B. Mid-level product – growing startup app
Features:
-
10–20 screens
-
Custom UI and some animations
-
In-app purchases, subscriptions, or payments
-
Push notifications
-
Basic offline capabilities
-
Analytics and maybe a small admin panel
Timeline:
Estimated cost of react native app:
- Around 40,000 – 90,000 USD
C. Complex / enterprise-grade app
Features:
-
Many flows and user roles
-
Advanced offline sync and conflict resolution
-
Real-time dashboards, chats, or collaboration
-
Multiple external APIs and internal system integrations
-
Advanced analytics and admin dashboards
Timeline:
- 6+ months, sometimes ongoing
Estimated react native development cost:
- 90,000 – 200,000+ USD, especially for long-term platforms
D. Comparison table
| Tier |
Example Features |
Est. Timeframe |
Est. Cost Range (USD) |
| Simple MVP |
Auth, profiles, simple lists, 1–2 integrations |
2–3 months |
15,000 – 40,000+ |
| Mid-level Product |
Custom UI, payments, notifications, analytics |
3–6 months |
40,000 – 90,000+ |
| Complex / Enterprise |
Multi-role, offline, real-time, dashboards, multiple APIs |
6+ months |
90,000 – 200,000+ (or more) |
These ranges help you anchor the react native app development cost conversation before you even write a brief.
Next, let’s see how team models and regions can move those numbers up or down.
Team Models, Regions, and Their Impact on React Native Development Cost
Two projects with the same scope can still have very different budgets depending on who builds them and where that team is.
A. Freelancers
Pros:
-
Flexible engagement
-
Often lower hourly rates
Cons:
-
You manage project, QA, and coordination
-
Risk if one person gets sick, busy, or leaves
Freelancers might bring down visible react native pricing per hour, but the total cost to build a react native app can rise if work is poorly coordinated or delayed.
B. In-house team
Pros:
Cons:
-
Salaries, hiring, tools, and overhead
-
Hard to scale up and down quickly
In-house makes sense when the app is central to your business and you expect ongoing work. Initial react native app cost may be higher, but long-term control improves.
C. Agencies / product studios
Pros:
-
Ready-made team with PM, designers, devs, QA
-
Clear process, estimates, and risk management
Cons:
- Higher apparent rate compared to solo freelancers
However, because you get structure and experience, total react native app development cost often ends up more predictable and sometimes even lower due to less rework.
D. Region-based cost differences
Short version:
But it’s not just about rate. Productivity, quality, time zones, and communication all affect the real react native app cost. Cheap hourly rate with lots of rework is not cheaper in the end.
If you prefer a full-stack product team instead of stitching freelancers together, partnering with a React Native Mobile App Development Company can give you clearer budgets, better planning, and fewer surprises as you move from idea to launch.
React Native Cross-Platform Development vs Pure Native – Cost Comparison
React Native is popular mostly because of its cross-platform nature. But what does that really mean for budget?
One shared codebase vs two separate codebases
With pure native:
-
You have two codebases (iOS and Android)
-
Two specialist teams or at least two skill sets
-
Most features built twice
With React Native Cross-Platform Development, you:
-
Share much of your UI and business logic
-
Implement platform-specific details only where needed
-
Maintain one main codebase and one core team
With react native app development company, you often get iOS and Android from largely one shared foundation, which directly lowers the react native development cost versus building everything twice.
High-level cost comparison
Roughly:
That gap is where a lot of react native pricing benefits come from, especially for MVPs and growing products.
Comparison table
| Approach |
Codebases |
Team Size |
Relative Total Cost |
| Pure native (iOS + Android) |
2 |
2 separate squads |
Highest |
| React Native cross-platform |
1 main |
1 core team |
Lower, especially for MVPs |
| Hybrid strategy (RN + some native) |
Mixed |
Mixed |
Depends on roadmap |
Of course, tools are only half the story. You still have to plan for hidden and ongoing costs after the first release.
Hidden & Ongoing Costs: Beyond the First Release
Many founders focus only on the initial build. But the real react native app development cost also includes what happens after you hit “publish”.
Maintenance and updates
You will need to:
-
Support new iOS and Android versions
-
Update libraries and dependencies
-
Fix bugs and small issues reported by users
Even a stable app needs time every few months to stay healthy.
Infrastructure and 3rd party tools
Ongoing costs include:
-
Backend hosting and databases
-
File storage, CDNs
-
Paid APIs like payment providers, SMS, email, analytics
These may not be huge at first, but they add up over time and should sit in your react native development cost planning.
Product growth and new features
If your app does well, you will want to:
A simple rule-of-thumb: plan yearly react native app cost for updates at around 15–25% of your initial build budget.
Why planning for ongoing cost avoids shocks
If you treat version 1.0 as the “end”, you will be surprised by future bills. Planning ongoing react native app development cost up front protects your roadmap and cash flow.
Step-by-Step: How to Estimate Your React Native App Development Cost
Let’s turn all this into something you can actually use in a spreadsheet or doc.
Step 1 – Define your MVP vs “nice to have”
-
List every feature you can think of
-
Mark each as Must-have, Nice-to-have, or Later
-
Cut hard. A smaller solid MVP means lower react native app cost and faster launch
Step 2 – Map screens and flows
-
Count key screens (onboarding, auth, home, detail, settings, etc.)
-
List complex flows separately (multi-step forms, booking flows, checkout)
-
More screens and flows = more hours, which increases react native development cost
Step 3 – Backend and integrations checklist
-
Decide if you need a custom backend or if BaaS is enough for first release
-
List all integrations: payments, maps, analytics, chat, CRM, etc.
-
Remove anything that you can truly live without for v1 to bring down cost to build a react native app
Step 4 – Pick team model and region
-
Decide: freelancers, in-house, or studio/agency
-
Estimate hours (with help) for each major area: design, frontend, backend, QA
-
Multiply by typical rates in your target region for a rough react native app cost
Step 5 – Add buffer and plan for phase 2
You can put this whole framework into a simple spreadsheet, adjust inputs, and compare options. If you want help turning it into a concrete estimate tied to your real idea and market, you don't have to guess that alone.
Cost Optimization Tips Without Killing Quality
You don’t control everything, but you can control how wisely you spend.
Prioritize features ruthlessly
-
Focus on a narrow core problem for version 1
-
Avoid building multiple “nice” features that users might not even touch
-
Less scope = lower react native app development cost and faster feedback
Reuse components and patterns
-
Build reusable UI components and logic early
-
Use a simple design system so new screens are quicker to build
-
This keeps react native pricing in check as you grow the app
Choose the right libraries (but not too many)
-
Use well-known, maintained packages for navigation, forms, etc.
-
Avoid adding a new dependency for every tiny thing
-
Fewer but solid dependencies reduce bugs and long-term cost of react native app
Start lean and iterate
-
Launch with a lean but reliable version
-
Measure real usage before adding expensive, complex features
-
This approach saves react native development cost that might otherwise go into things users don’t need
Now, let’s clear a few quick questions founders ask again and again.
Conclusion – Turn React Native App Cost into a Clear Roadmap
React Native is a strong choice for cross-platform apps in 2026. It helps you reach iOS and Android with one main codebase and gives a solid balance between performance, speed, and cost. But there’s no single magic number for react native app development cost. It depends on features, design depth, backend, team model, and how committed you are to growing the product after launch.
The good news is that with a structured approach, you can move from vague guesses to a clear, phased roadmap and a realistic budget. Start by defining your MVP, mapping screens and flows, and picking a team model that fits your stage and risk appetite.

Tags
App Development Cost
Cross Platform
React Native
App Development



 Facebook
Facebook
 Twitter
Twitter
 LinkedIn
LinkedIn
 Pinterest
Pinterest