If your odds are even two seconds late, you don’t have a “performance issue.” You have a pricing risk, a liability problem, and a trust problem. A sportsbook isn’t a normal app. It’s a regulated, real-time financial system that happens to look like a mobile product.
In the U.S. alone, legal sports betting revenue climbed to about $13.78B in 2024, with Americans placing roughly $149.90B in legal bets. Globally, the sports betting market was estimated at around $100.9B in 2024 and is projected to keep growing through 2030.
This guide is for enterprise teams and startups that need clarity on how to develop a sports betting app without guessing. We’ll cover sports betting app development steps, real-time odds integration, AML compliance, PCI compliance, architecture decisions, and realistic cost drivers.
Define the Sports Betting Product You Are Building
Before you talk features, you need to define what you’re shipping. “Sports betting app” gets used as a blanket term, but the product model changes the tech, the compliance load, and the business risk.
Sportsbook vs Fantasy vs Exchange (Quick Distinctions)
- Sportsbook (traditional betting): You offer markets and set odds (or ingest odds), users place bets, you manage exposure, and you settle outcomes.
- Fantasy (DFS): Users create lineups; outcomes depend on player performance. It can be regulated differently depending on jurisdiction, but it’s still compliance-heavy.
- Betting exchange: Users bet against each other (peer-to-peer). This adds market-making mechanics, liquidity challenges, and a different risk surface.
If your roadmap includes fantasy sports app development as a parallel product, plan it as a separate track. The data model, gameplay loops, and regulatory approach often diverge early.
Core Subsystems You’ll Need (No Matter the UI)
A modern sportsbook platform usually breaks into these core domains:
- Odds & markets: ingestion, normalization, pricing updates, market states.
- Bet slip & bet placement: validation, acceptance rules, idempotency.
- Wallet & payments: ledger, deposits, withdrawals, holds, reversals.
- Risk & trading controls: exposure, limits, suspicious patterns, overrides.
- Settlement: results ingestion, bet grading, payouts, refunds, disputes.
- Admin & reporting: user/KYC actions, fraud flags, revenue reporting.
- Compliance & audit: KYC/AML workflows, logs, retention, exports.
Product Type vs Complexity vs Compliance Load
| Product Type |
Typical Complexity |
Real-Time Requirements |
Compliance Load |
| Sportsbook |
High |
Very high (live odds) |
Very high |
| Fantasy (DFS) |
Medium–High |
Medium |
High (varies by region) |
| Exchange |
Very high |
Very high (market liquidity) |
Very high |
This matters because building a sportsbook app isn’t really a design goal, but an operational goal, and you’re signing up for real-time risk management, wallet correctness, and audit readiness.
Benefits of Sports Betting App Development
Building a sportsbook isn’t just “making an app,” but also building a direct revenue channel that you control end-to-end. For startups, it helps you launch, measure, and improve faster. For enterprises, it supports standardization, compliance readiness, and scalable operations without losing user trust.

Here’s why creating a sports betting app is worth it for businesses:
1. Customer Ownership
You control the full user journey inside your platform:
- Onboarding and verification flows
- Promotions, loyalty, and segmentation
- Notifications and lifecycle messaging
- Support, disputes, and refunds
This matters because retention and repeat betting are what drive profitability over time.
2. Retention Strength
Betting apps create natural return visits through:
- Live matches and frequent market updates
- New odds and bet opportunities
- Bet outcomes, payouts, and cashout options
- Event-driven promotions
Retention only holds if the platform stays stable during traffic spikes and settlements are accurate.
3. Faster Iteration
A well-built sportsbook supports controlled releases:
- Feature flags for phased rollout
- Experimentation for UX and conversion improvements
- Rapid tuning of limits and promotions based on performance
Enterprises benefit because changes can be governed and audited, not pushed blindly.
4. Margin Control
A modern platform improves operational control over risk and revenue:
- Stake limits and max payout rules
- Exposure tracking across events and markets
- Fraud and bonus abuse detection
- Consistent enforcement through a risk engine
This prevents “high growth, low profit” outcomes.
5. Compliance Advantage
When compliance is designed into the product early, scaling becomes easier:
- Streamlined KYC review workflows
- AML compliance monitoring and case handling
- Responsible gambling controls
- Audit logs and reporting exports
In regulated markets, this reduces launch friction and increases partner trust.
6. Live Betting Readiness
Live betting becomes a growth lever only when real-time behavior is reliable:
- Real-time odds integration with low latency
- Clear price-change confirmation flows
- Stable bet placement under load
- Accurate wallet and settlement processing
Without these controls, live betting increases disputes and support costs.
7. Long-Term Scalability
A compliance-ready and production-grade platform becomes a durable asset:
- Easier expansion into new sports and markets
- Smoother partner and vendor integrations
- Fewer outages during high-volume events
- Stronger trust with regulators and users
That’s the long-term value of building the foundation correctly.
How to Develop a Sports Betting App Step-By-Step
Building a sportsbook app is a strategic arrangement of market insight, regulatory compliance, and robust technology. Top operators treat app development as an end-to-end process that spans market research, compliance planning, UX design, system architecture, and rigorous testing.
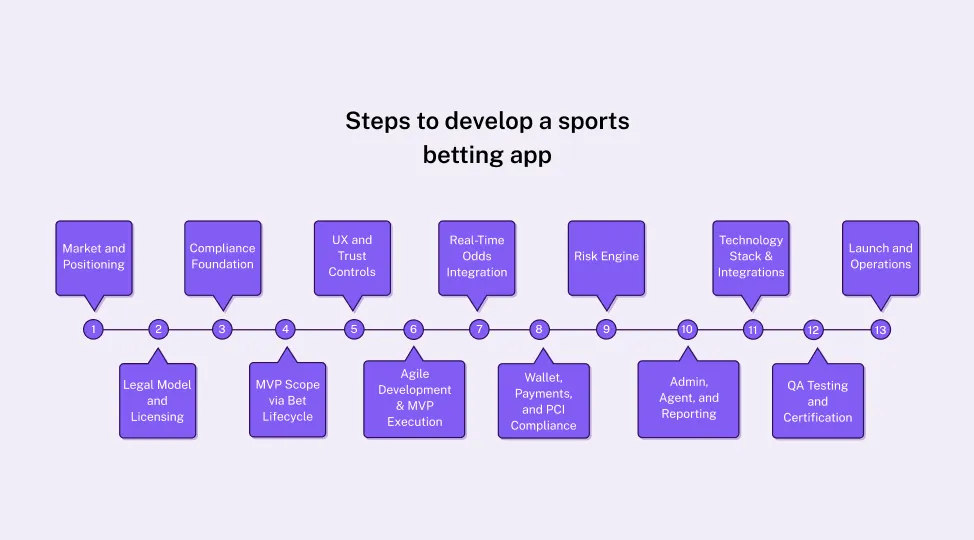
Here’s the detailed breakdown of the 13 structured sports betting app development steps that reflect how leading sportsbooks approach app development as of 2026.
Step 1: Market and Positioning
Start with the uncomfortable truth: you’re not competing on UI, but on trust, speed, and payouts. This is where you decide what “win” looks like for your users and your business.
Choose your target market first
- Jurisdiction(s), sports coverage, bet types you will support at launch
- A single state or region is often smarter than “global on day one”
Define your wedge
- Faster live betting, better payouts, better promos governance, better UX clarity
Benchmark against leaders
- Use FanDuel, DraftKings, BetMGM as baselines, not as templates
- If your goal is to build a sportsbook app like FanDuel, focus on the live flow, bet slip stability, and confirmation speed. Not the animations.
Set measurable KPIs
- Time-to-bet, bet placement success rate, deposit success rate
- Settlement accuracy and payout turnaround time
- Fraud rate, bonus abuse rate, chargeback rate
This step is where enterprise teams align stakeholders. Startups skip it and later wonder why priorities fight each other.
Step 2: Legal Model and Licensing
Licensing is not a line item because it shapes product scope, data flows, and launch timelines.
Pick your operating model:
- Licensed operator
- Partner with an operator
- White-label
Then map what changes under each:
- Who owns KYC decisions
- Who runs AML compliance operations
- Who is the merchant of record for payments
- Who is accountable for regulatory reporting and audits
Write this down early, as your architecture depends on it.
Step 3: Compliance Foundation
This is the part many teams try to “add later.” It never works cleanly, and the reason is simple: compliance controls are tied to identity, money movement, and auditability.
Minimum foundation:
KYC in the onboarding flow
- Identity verification states (pending/approved/failed) should be product-visible
- Manual review queue, document handling, retention rules
AML compliance workflows
- Transaction monitoring, alert queues, escalation, resolution notes
- Evidence trails and reviewer accountability
Responsible gambling
- Limits, cooling-off, self-exclusion, reality checks
- Enforcement that can’t be bypassed by simple app tricks
If you want to understand how to develop sports betting app products for regulated markets, treat compliance like core UX. Because it is.
Step 4: MVP Scope via Bet Lifecycle
Sportsbooks fail when MVP is defined as “login & odds & bet button.” That’s not a sportsbook. A sportsbook is the lifecycle.
A simple bet lifecycle looks like this:
- Market open, then odds update, then bet placed, then accepted/rejected, then settled, and finally paid/refunded.
Use it to decide scope:
MVP must-haves
- Pre-match markets, basic live markets (limited), bet slip, wallet, settlement, admin controls
Phase 2
- Advanced promos, complex parlays, live streaming, deep personalization, bonus automation at scale
This step keeps your roadmap realistic. It also keeps mobile app development cost from exploding due to “just one more feature.”
Step 5: UX and Trust Controls
A sportsbook UX is not about being clever, but about reducing mistakes and disputes.
Core UX controls that matter:
-
Price-change confirmation before bet placement (clear, consistent)
-
Clear bet status (accepted, pending, rejected) with reasons
-
Withdrawal friction where needed:
Not annoying friction. Defensive friction that prevents fraud and disputes.
-
Responsible gambling UX:
Limits and self-exclusion should be easy to find and easy to enforce
This is where product teams earn credibility. Users can forgive a basic interface, but they won’t forgive confusion around money.
Step 6: Agile Development & MVP Execution
With blueprints approved, start coding using agile sprints. Begin by building a minimum viable product (MVP), which is the simplest working sportsbook.
Core early deliverables typically include:
- Wallet & Account Systems: Secure user accounts with deposit/withdraw and wallet logic.
- Bet Placement Service: The engine that accepts a bet, validates it against rules, and records it.
- Risk Management Modules: Even in MVP, implement basic limits (max bet amounts, auto-validation) to prevent runaway losses.
- Admin Dashboard: A back-office UI to monitor bets, manage markets, and handle support tickets.
Crucially, build in compliance layers from day one. Integrate KYC/AML checks (identity verification APIs, transaction monitoring) and ensure payment processes meet PCI-DSS standards.
A staged MVP deployment (perhaps in a single test region) lets you validate performance under moderate load before unlocking every feature. In practice, operators often release a controlled beta to make sure the system holds up and to refine real-time betting flows.
Step 7: Real-Time Odds Integration
Real-time odds integration is where sportsbooks turn into engineering systems. You’re ingesting high-frequency updates, then presenting a stable view of markets to users under load.
Key decisions:
Choose the data provider(s):
- Coverage, latency, uptime track record, update method (push vs pull)
Define your update strategy
- Streaming ingestion & normalization layer (don’t push raw feeds straight to the app)
- Caching strategy for market pages and bet slip
Handle spikes and partial outages
- Retries with backoff, circuit breakers, backpressure
- Degraded mode: show last-known odds with clear status, suspend markets safely
Protect bet placement
- Use idempotency keys so a user doesn’t place the same bet twice
- Validate market state at acceptance time, not just at display time
If the goal is how to develop a sports betting app that survives peak events, this is the non-negotiable step.
Step 8: Wallet, Payments, and PCI Compliance
The wallet is your system of record. Payments are how money enters and exits. Mixing those responsibilities causes reconciliation nightmares and audit problems.
Core wallet principles:
Ledger-first design
- Every balance change is an entry with reason codes
- Separate available vs held funds (for unsettled bets)
Payout flows
- Track payout states (initiated, pending, completed, failed) with evidence
PCI compliance boundaries
- Avoid storing raw card data
- Use tokenization with a PCI-compliant gateway
- Keep payment processing isolated from the core wallet ledger
PCI compliance is easier when you design for it upfront. Retrofitting it later is expensive and messy.
Step 9: Risk Engine
You can launch without “fancy AI.” You cannot launch without risk controls. Risk is not only fraud, but also exposure and pricing volatility.
Minimum risk capabilities:
Limits
- Stake limits, max payout, per-market caps, per-user caps
Exposure tracking
- Exposure by event, market, user segment, and time window
Suspicious behavior signals
- Rapid deposit/withdraw cycles, multi-account patterns, promo abuse
Manual review
- Escalation workflows and action logging (who did what, and why)
This is where sportsbooks protect margin. It’s also where compliance teams gain confidence in operations.
Step 10: Admin, Agent, and Reporting
Your admin panel is not an internal dashboard, but the control tower. It needs audit trails, permissions, and safe operational tools.
Admin must-haves:
- User management, KYC review, account actions (with audit logs)
- Market controls (open/suspend/close) with reasons and history
- Settlement tools and overrides with strict permissions
- Reporting: revenue, exposure, payout health, fraud signals, promo spend
Agent panel (only if your model needs it):
- Attribution, commissions, user mapping, role-based access
- Anti-fraud controls around payouts and referrals
Skipping this is how startups ship a demo, not a platform.
Step 11: Technology Stack & Integrations
At this point, choose the final development stack and integrate third-party services. Stack choices should align with performance needs and long-term scaling.
Common industry choices include:
Frontend Cross-platform frameworks (React Native, Flutter) can speed mobile development, but high-performance apps may use native (Kotlin/Swift) for ultimate Android and iOS app development.
Backend: Popular stacks include Node.js, Python/Django, or Java/Spring. Architect your services with containers (e.g. Docker) and orchestration (Kubernetes) for easy scaling. Monolith-vs-microservices trade-off depends on team expertise, so, pick what your team can maintain.
Database: Relational (PostgreSQL, MySQL) for transactional data, plus NoSQL (MongoDB) or in-memory (Redis) caches for fast read/writes. Plan for sharded clusters and read replicas to handle peak loads.
Third-Party Integrations:
- Odds and Sports Data: Partner with real-time data providers (OddsAPI, Sportradar, etc.).
- dentity Verification: Use KYC/AML APIs (e.g. Jumio, Onfido) to verify users.
- Fraud Detection: Integrate fraud analytics engines to flag suspicious patterns
- Payments: Connect multiple gateways (Stripe, PayPal, local e-wallets, even crypto) and ensure redundancy so users aren’t stranded by a single payment outage.
All integrations must support the concurrency demands of a sportsbook. Select messaging or API frameworks such as gRPC, REST, or WebSockets that can handle thousands of real-time updates per second.
Whether you are leveraging cross-platform frameworks or specialized Android or iOS app development services for performance-critical builds, the backend stack must align with your expected user load and feature roadmap to ensure scalability and low latency.

Step 12: QA Testing and Certification
Testing a sportsbook is not “click around and ship.” You test for concurrency, money correctness, and failure modes.
Your QA process should include:
Load and Stress Testing: Simulate tens of thousands of concurrent users placing bets. Replicate peak scenarios (e.g., Super Bowl, World Cup final) with spiking traffic. Auto-scaling groups and load balancers are essential to handle event-driven surges. Adjust resources until the system handles heavy load without errors or unacceptable latency.
Performance Testing: Verify that real-time components (odds updates, websocket feeds) stay within acceptable latency bounds. Ensure your database doesn’t lock up under burst writes (bet placements) by testing high volumes.
Security Testing: Conduct penetration tests, attempt transaction replays, and deliberately feed malformed data to identify weaknesses. Test fraud detection by simulating abnormal betting patterns or multi-account scenarios.
Compliance Testing: Confirm that geo-blocking, age checks, and limit triggers work under stress. Audit all log entries to ensure completeness.
Beta Testing: Run a live beta with a small user group (or in a sandbox region) to catch UX glitches or workflow issues not seen in earlier sprints.
Wallet correctness
- Holds, settlements, partial refunds, reversals, reconciliation
Security
- API abuse, bots, account takeover attempts, admin privilege misuse
Compliance verification
- Evidence trails for KYC and AML compliance cases
- Geo enforcement behavior in edge conditions
Thorough testing will catch the bottlenecks and bugs that coding sprints might miss. It’s critical because any downtime, settlement error, or exploit on launch day could mean lawsuits or license suspension. Don’t ship until QA has pounded the system into submission.
Robust load testing and monitoring prepare your app to handle peak betting events (e.g., major games) without failure.
Step 13: Launch and Operations
Launching is when reality shows up. A strong sportsbook launch looks boring from the outside. That’s the point.
Operational launch essentials:
Soft launch with feature flags
- Limit markets, limit bet sizes, monitor stability, expand gradually
Rollback strategy
- Clear paths to disable live markets, disable certain providers, or pause withdrawals safely
Monitoring
- Odds latency, bet acceptance failures, payout failures
- Fraud spikes, promo abuse signals, settlement anomalies
If you’re serious about how to develop a sports betting app for enterprise scale, operations is part of the product. Always has been.
Core Features Required in a Modern Sports Betting App

A modern sportsbook isn’t defined by how pretty the home screen looks, but by whether users can place bets reliably, whether settlement is correct, and whether you can prove compliance under scrutiny.
The clean way to scope features is by panel: user experience, operator controls, risk controls, and platform foundations.
User App (What Players Touch Every Day)
1. Onboarding & Identity
- Email/phone sign-up, secure login, device binding
- 2FA for sensitive actions (withdrawals, password reset)
- KYC intake flow with clear status states (pending/approved/failed)
2. Sports Discovery & Markets
- Sports/leagues browsing, event pages, market grouping
- Fast search and favorites (teams, leagues, bet types)
- Market status clarity (open, suspended, closed)
3. Bet Slip & Bet Placement
- Single and parlay support with transparent odds math
- Price-change confirmation rules (don’t “surprise” users)
- Bet validation before acceptance (limits, market state, wallet balance)
4. Live experience
- Live odds display with stable refresh behavior
- Live scores and key match events (drive decision-making)
- Real-time odds integration that handles spikes without freezing the app
5. Wallet & payments
- Deposits, withdrawals, transaction history, receipts
- Clear “available vs on-hold” balances (users fight you less when it’s clear)
- Payout status tracking and resolution workflows
6. Responsible gambling controls
- Deposit limits, time limits, cooling-off, self-exclusion
- Reality checks and safer gambling prompts (kept respectful, not preachy)
Admin Panel (Where You Actually Run The Business)
This is where many teams cut corners, then regret it later. Admin is not a “nice-to-have.” It’s the operating system of the sportsbook.
1. User & Account Controls
- Account status actions (review, suspend, close) with audit logs
- KYC document review queues, re-verification workflows
- Case notes and evidence attachments (for disputes and compliance)
2. Market and bet operations
- Market state controls (open/suspend/close) with reasons
- Bet settlement tooling, overrides with strict permissions
- Dispute handling and refund controls with traceability
3. Compliance workflows
- AML compliance review queues (alerts, escalation, approvals)
- Reporting exports and retention controls (who accessed what, when)
- Responsible gambling support actions (limit enforcement, exclusions)
4. Business reporting
- Revenue dashboards, promo spend, user cohorts
- Exposure reports by event/market
- Payment success rates, payout delays, and chargeback tracking
Risk & Trading Tools (How Sportsbooks Avoid Getting Crushed)
1. Limits & Exposure Management
- Stake limits, max payout rules, and per-market caps
- Exposure tracking by event, market, and user segment
- Automated restrictions for volatile events
2. Suspicious Behavior Detection
- Multi-accounting signals, bonus abuse patterns
- Arbitrage signals (not perfect, but useful)
- Velocity controls (rapid deposits, rapid withdrawals, repeated failures)
3. Manual Controls
- Trader overrides and approvals for high-risk markets
- Reason codes on actions (helps audits and internal reviews)
Agent Panel (If Your Model Uses Agents Or Affiliates)
- Agent onboarding, attribution, commission rules
- User mapping and performance reporting
- Role-based access, payout visibility, and fraud controls
Platform Essentials (The “Invisible” Features That Decide If You Survive)
These aren’t glamorous, but they determine stability and trust.
1. Audit Logs & Access Control
- Role-based access (RBAC), least-privilege defaults
- Immutable-ish audit trails for admin actions and settlement changes
2. Reliability and observability
- Monitoring for odds latency, bet acceptance failures, and settlement failures
- Alerting for provider outages, payment drop-offs, and fraud spikes
- Incident playbooks and rollback strategies
3. Payments posture
- PCI compliance boundaries (tokenization, storage rules, vendor scope)
- Clear separation between the wallet ledger and the payment processing
- Dispute handling with evidence capture and traceable decisions
This feature set is also why the mobile app development cost can swing wildly. A “basic app” is cheap, but a compliant sportsbook with real-time risk controls is not.
Address Global Compliance and Regulatory Requirements Early
Compliance isn’t a “phase after MVP.” It’s part of the product definition because licensing rules decide what you can ship, how you verify users, how you store data, and how you settle bets. To develop a sports betting app, you must build compliance controls into the first release.
1. Licensing Models
Your licensing path drives your operating model. Most teams land in one of these three buckets:
- Licensed operator: You hold the license. You own KYC, AML compliance processes, reporting, and most of the liability.
- Partner with a licensed operator: You build the product, but operate under a partner’s license and controls. Faster to market, but you inherit constraints.
- White-label: You deploy on someone else’s platform. Speed is high, differentiation is limited, and your data/control surface can be smaller than you expect.
This decision changes who “owns” payments, who files regulatory reports, who is accountable for suspicious activity monitoring, and who answers when audits happen. Getting this wrong early makes the later rebuild painful.
2. KYC
KYC is not just “upload an ID,” but also a workflow with states, evidence, and repeatability.
Core KYC capabilities usually include:
- Identity & age verification (with re-check triggers when risk increases)
- Document capture and handling (secure storage, access logging, retention rules)
- PEP/sanctions screening at a high level, depending on jurisdiction and provider setup
- Manual review queues and clear outcomes (approved, failed, needs more info)
If you’re mapping how to develop a sports betting app across multiple regions, assume your KYC flow will branch. What’s acceptable in one market may be insufficient in another.
3. AML Compliance
AML compliance is where betting apps get into real trouble, because the money movement is constant and the patterns can look “normal” until they’re not. Most regulators expect a risk-based approach: you tailor controls to your customer base, products, and exposure profile.
At a practical level, AML compliance typically means:
- Transaction monitoring (velocity checks, unusual deposit/withdraw behavior, structuring signals)
- Case management (alerts, then review, then action, then notes/evidence, and finally resolution)
- Audit-ready logs (who reviewed, what they saw, what decision they made)
- Escalation workflows for higher-risk activity
If you want a clean execution path for how to develop a sports betting app, treat AML as a product requirement: queues, states, evidence, permissions, and reporting. Not a policy PDF sitting in a folder.
4. Responsible Gambling
Responsible gambling controls aren’t just for optics. They reduce chargebacks, disputes, and regulator heat, and they protect the long-term viability of the product.
Common required capabilities:
- Deposit and loss limits
- Cooling-off periods and timeouts
- Self-exclusion
- Reality checks and safer gambling messaging
- Support escalation when risky behavior thresholds are crossed
Build these as first-class features, with tracking and enforcement that’s hard to bypass.
5. Payments and PCI Compliance
Payments are a compliance boundary, not only a feature. If your system stores, processes, or transmits cardholder data, you’re in PCI DSS scope, and that impacts architecture decisions immediately.
Ways teams reduce PCI scope (while staying realistic):
- Use a PCI-compliant payment provider and avoid storing raw card data
- Use the tokenization patterns provided by the gateway
- Separate the wallet ledger (your system of record) from payment processing systems
- Lock down access, logging, and retention around payment-related events
PCI compliance is easier when your product never touches sensitive card data directly, and you keep clean boundaries between services.
6. Geo and Data Rules
Most regulated markets expect location enforcement, and many expect strong evidence trails.
Key capabilities:
- Geolocation enforcement (and handling edge cases like weak signals)
- Anti-bypass basics (flagging risky sessions, suspicious device patterns)
- Data governance: retention, access logs, exportability for audits
- Jurisdiction-specific reporting readiness (formats and cadence vary)
For remote/online operators, regulators publish guidance and technical expectations that influence product controls and operational processes.
Compliance Checklist (Box)
Use this as the baseline “done means done” list:
- Licensing model finalized (operator/partner/white-label)
- KYC workflow implemented (states, evidence, queues, retention)
- AML compliance workflows implemented (monitoring, cases, audit logs)
- Responsible gambling controls enforced (limits, exclusions, messaging)
- PCI compliance scope defined and minimized (gateway & tokenization strategy)
- Geolocation rules enforced and logged
- Admin permissions locked (RBAC, least privilege, immutable-ish audit trails)
Design a Production-Ready Architecture for Real-Time Betting
When evaluating how to develop sports betting app platforms that scale beyond MVP stage, the real differentiator is architecture. The gap between a basic betting app and an enterprise sportsbook is not features, but the ability to handle unpredictable traffic spikes, real-time volatility, and strict regulatory auditing.
In 2026, sports betting app development demands architecture-first thinking, where infrastructure decisions directly determine revenue stability, compliance readiness, and long-term scalability.
Core Services
Identity & KYC service
- Account creation, verification states, document workflows, access logging
Odds ingestion service
- Normalizes provider feeds into your internal market model
- Handles suspensions, stale odds, provider failover rules
Betting service
- Bet slip validation, acceptance rules, idempotency keys, bet state transitions
Wallet/ledger service
- The source of truth for balances, holds, settlements, reversals
- Keeps transaction trails consistent (audit-friendly by design)
Risk engine
- Limits, exposure tracking, suspicious patterns, manual review triggers
Settlement service
- Results ingestion, grading rules, payout calculations, dispute workflows
Promotions/bonus service (optional early)
- Controlled promo rules, abuse prevention hooks, audit logging
Notifications service
- Bet confirmations, odds change prompts, settlement updates, RG notices
Reporting & audit service
- Immutable-ish audit trails, exports, regulator-ready reporting views
This separation also makes it easier to scale teams. Startups move faster, enterprises reduce blast radius when something breaks.
Data Layer Choices (What Stores What)
Most sportsbook failures happen when the wrong data ends up in the wrong store, or when “eventual consistency” leaks into money.
Relational database (PostgreSQL/MySQL)
- Best place for wallet ledger, bets, settlement records, and audit-critical data
Cache layer (Redis or equivalent)
- Fast reads for odds/markets and sessions, with strict TTLs to avoid stale confidence
Event streaming (Kafka or equivalent)
- Odds updates, bet events, settlement events, fraud alerts, payment state changes
- Helps decouple services so one slow consumer doesn’t stall the whole platform
Object storage
- KYC documents, receipts, evidence attachments, archived logs
Build Pattern Choice (Modular First, Then Split)
Most of the teams argue among monolith vs microservices. But, the better question is: how do you ship safely.
Modular monolith (often best for MVP)
- Faster delivery, fewer distributed failures, easier to test end-to-end
- Works well if your boundaries are clean (wallet module, betting module, etc.)
Microservices (when scale and org demand it)
- Useful when different domains need independent scaling and independent deployments
- Requires real maturity in observability, CI/CD, and incident response
Event-driven patterns are commonly used to keep services decoupled by publishing and consuming events instead of direct tight coupling.
High Availability Basics (Non-Negotiable)
- Multi-zone deployment for critical services (wallet, betting, settlement)
- Queues and retries with backoff for external integrations (odds, KYC, payments)
- Circuit breakers and degraded-mode behavior (suspend markets safely, don’t guess)
- Observability that measures what matters: odds latency, bet acceptance time, settlement failures
For a sportsbook, “degraded mode” should be designed. Not improvised.
This architecture supports what an experienced sports betting app development company promises in plain business terms, i.e., real-time odds, seamless betting flows, and compliant operations, but backed by systems that can actually sustain them.
Implement Security Controls That Match Financial-Grade Risk
Security is not a checklist you paste in at the end. In betting, security is revenue protection, compliance protection, and brand protection. To develop a sports betting app for 2026, you need to treat every bet and every balance change like it belongs in a bank ledger.
Threat Model (What Actually Goes Wrong)
A sportsbook gets attacked in predictable ways. The names change, the patterns don’t.
- Account takeover (ATO): credential stuffing, SIM swaps, session hijacking, OTP abuse
- Bot betting: automated bet placement, scraping odds, abusing promos
- Promo and bonus abuse: multi-accounting, referral farming, arbitrage behaviors
- Payment fraud: stolen cards, chargebacks, laundering through deposits/withdrawals
- Admin abuse: overpowered roles, weak audit trails, “silent” settlement changes
- API abuse: broken authorization, broken authentication, data exposure, unsafe API consumption.
Security Controls
1. Strong identity and session controls
- Enforce MFA for sensitive actions (withdrawal, password change, device change). NIST’s AAL2 guidance is a good baseline for two-factor authentication expectations.
- Device fingerprinting and step-up verification for risky behavior (new device & large withdrawal, for example)
- Short-lived tokens, secure refresh patterns, and session revocation that actually works
2. API security that assumes hostile traffic
- Object-level authorization on every endpoint that touches user-owned resources (OWASP calls this out hard because it’s so commonly broken).
- Rate limiting per user, per device, and per IP range; add bot defenses at the edge
- Input validation and anti-injection controls aligned to OWASP Top 10-style failure modes
- Inventory and monitor every API surface, including internal ones (APIs don’t stay “internal” for long)
3. Wallet and settlement integrity controls
- Ledger-first accounting with immutable-style event trails (append-only where possible)
- Idempotency keys on bet placement and payment updates, so retries don’t double-charge or double-bet
- Strict separation of duties: settlement overrides should require elevated permissions and reason codes
- Reconciliation jobs that detect drift between wallet, provider events, and settlement outcomes
4. Least privilege for admin and support teams
- Role-based access (RBAC) with least privilege as default
- Strong logging for every admin action: who, what, when, and why
- Privileged access reviews on a schedule.
5. Observability and incident response
- Track what matters: odds latency, bet acceptance time, payment failures, settlement anomalies
- Alerts that route to humans with clear playbooks.
- Degraded mode rules: suspend markets safely, delay cashouts, pause withdrawals when signals spike
Sports Betting Mobile App Development Cost in 2026
Sports betting app development cost in 2026 is driven by architecture complexity, regulatory exposure, real-time infrastructure requirements, and long-term scalability expectations.
The key cost drivers include:
- Licensing and jurisdictional compliance scope
- Real-time odds engine and data provider integrations
- Microservices architecture vs modular backend design
- Security layers covering AML compliance and PCI compliance
- Cloud infrastructure designed for peak concurrency
The following breakdown will help you determine where your sportsbook vision fits, from validation-stage MVP to enterprise-scale infrastructure.
These estimates reflect development complexity, backend engineering depth, and integration requirements.
| Development Tier |
Estimated Cost Range |
What It Includes |
| Basic MVP Platform (3–5 months) |
$30,000 – $70,000 |
Single sport, user registration, basic bet placement, manual or basic scoring, simple admin panel. Ideal for early validation and limited market launch. |
| Growth-Ready / Mid-Range MVP (5–7 months) |
$70,000 – $120,000 |
Multiple sports, real-time odds API integration, secure payment wallets, improved UI/UX, backend scalability. Designed for operators preparing for market expansion. |
| Complex-Level Custom Platform |
$120,000 – $200,000+ |
Live betting, multi-sport support, real-time data feeds, secure payments, stronger compliance controls, customized iOS/Android apps, scalable backend infrastructure. |
| Enterprise-Grade Platform (6–12+ months) |
$180,000 – $400,000+ |
AI-driven analytics, live streaming, multi-currency support, advanced risk management, high-security architecture, real-time trading engine, multi-jurisdiction readiness. |
- Platform Development (Frontend & Backend): $60,000 – $120,000+
- UI/UX Design: $15,000 – $30,000+
- Third-Party Integrations: $25,000 – $50,000+ (odds APIs, payment gateways, KYC)
- Compliance & Security: $20,000 – $40,000+
- AI / Advanced Risk Systems (Enterprise): Additional cost depending on scope.
Ongoing Maintenance
Post-launch operational costs typically range between 15% to 25% of the initial development cost per year. This includes:
- Infrastructure hosting
- Security updates
- Compliance audits
- Feature enhancements
- Performance optimization
While white-label platforms reduce initial mobile app development cost, custom platforms provide greater long-term control and scalability potential.
Strategic cost planning ensures sustainable growth rather than short-term market entry.
💡Suggested Read: A Detailed Guide to Sports Betting App Development Cost
Timeline to Build a Sports Betting App
A typical enterprise-grade sports betting app development roadmap progresses through discovery, architecture design, engineering, and scaling. Each phase builds on regulatory validation and infrastructure readiness.
- Discovery Phase – 4 to 6 Weeks: This stage defines market positioning, licensing scope, feature prioritization, and infrastructure requirements. Technical feasibility and compliance obligations are mapped before active development begins.
- Architecture Design – 3 to 4 Weeks: Engineering teams design microservices segmentation, database models, real-time processing flows, and integration blueprints. Architectural clarity at this stage reduces future scalability bottlenecks.
- MVP Development – 3 to 5 Months: Core modules such as wallet systems, real-time odds integration, onboarding with AML compliance, and bet placement services are implemented. Agile iterations ensure performance validation during development.
- Testing and Validation – 4 to 6 Weeks: Load testing, security audits, and compliance verification ensure production readiness. Systems must demonstrate stability under high concurrency.
- Deployment and Initial Scaling: After launch, monitoring frameworks and auto-scaling policies are activated. Early traffic insights inform infrastructure adjustments.
White-Label vs Custom Timeline
White-label solutions can launch within 2 to 4 months due to pre-built modules. Custom platforms typically require 6 to 12 months but provide architectural control, performance optimization, and regulatory flexibility necessary for long-term growth.
Realistic planning ensures that launch speed does not compromise scalability or compliance integrity.
Why Sports Betting Apps Fail: 5 Common Development Mistakes to Avoid
Even well-funded operators encounter avoidable setbacks when architecture and governance are not prioritized early. Preventing these errors protects scalability, compliance standing, and long-term profitability.
- Ignoring Compliance Early: Treating AML compliance and PCI compliance as post-development add-ons creates systemic risk. Retrofitting transaction monitoring, audit logging, and geo-validation mechanisms increases cost and delays licensing approval. Compliance must be embedded into the architecture from the outset.
- Poor Database Design: Relying on a single database model for both financial transactions and high-frequency read operations creates bottlenecks. Without proper segregation between relational transaction systems and scalable read-optimized storage, latency escalates under load. Database misalignment becomes visible during live betting spikes.
- Weak Security Practices: Insufficient encryption, improper access controls, and limited monitoring expose sportsbooks to fraud, data breaches, and regulatory penalties. Financial platforms demand layered security architecture, not basic application-level protections.
- Inadequate Load Testing: Failing to simulate peak concurrency conditions leads to downtime during major events. Without aggressive stress testing of real-time odds integration and bet placement services, live tournaments can overwhelm infrastructure.
- Over-Reliance on White-Label Solutions: White-label platforms reduce initial mobile app development cost, but they often limit scalability, customization, and compliance flexibility. Operators seeking long-term differentiation may encounter integration constraints and vendor lock-in.
Avoiding these mistakes requires disciplined architectural planning, compliance foresight, and production-grade engineering from day one.
Top Use Cases of the Market Leaders
These are use cases you can borrow as product patterns. Each one describes a real user moment, the flow that supports it, and what “success” looks like from the user’s side.
FanDuel: Live Betting During a High-Tempo Game
Primary user: a repeat bettor who wants speed, confidence, and minimal friction.
Scenario: A user is watching a close game. They want to place multiple live bets as momentum shifts, without feeling like the app is lagging or tricking them.
Typical Flow (User-Side)
- Opens live game
- Scans live markets quickly (spread/total/player props)
- Adds selections to bet slip
- Confirms if odds moved (price change prompt)
- Places bet and gets instant confirmation
- Tracks active bets and outcomes in real time
What The User Expects
- Markets load fast and don’t “jump” unpredictably
- The bet slip feels stable, not fragile
- Confirmations are immediate and clear
- The app never makes them wonder if the bet actually went through
Success Signals
- Short time-to-bet
- High bet completion rate
- Low “failed bet” / “pending too long” frustration
DraftKings: Same-Game Combinations for Higher Engagement
Primary user: a more engaged bettor who enjoys building combinations and optimizing outcomes.
Scenario: A user wants to build a same-game set of outcomes (multiple events tied to one match) because it feels more strategic and more personal than a single wager.
Typical fFow (User-Side)
- Opens an event page
- Builds a multi-selection bet (within the same event)
- Reviews combined odds and risk/reward
- Adjusts selections based on rules and constraints
- Places the bet, then tracks outcomes across selections
What The User Expects
- Clear rules and constraints (why a selection can’t be combined)
- Transparent payout math
- A clean “review” moment before commit
- A simple way to follow progress across selections
Success Signals
- High multi-selection adoption
- Low confusion during “can’t combine” moments
- Strong repeat rate for the same flow (habit formation)
BetMGM: Trust-First Betting for Broad Audiences
Primary user: a mainstream bettor who cares most about reliability, payouts, and support.
Scenario: A user deposits funds, places a few bets, and later withdraws winnings. They care less about fancy features and more about the product feeling legitimate and consistent.
Typical Flow (User-Side)
- Creates account and verifies identity
- Deposits funds
- Places pre-match and occasional live bets
- Checks results and settlement history
- Withdraws winnings and tracks payout status
- Contacts support if something looks off
What The User Expects
- Smooth onboarding and verification updates
- Deposits and withdrawals that feel predictable
- A clear history trail: bets, wins/losses, adjustments
- Support paths that don’t feel like a maze
Success Signals
- High deposit success rate
- Low payout complaints
- Low dispute rate driven by unclear settlement or missing history
What Each Use Case Emphasizes
| Use Case Pattern |
User Priority |
What “Good” Feels Like |
What Breaks Trust Fast |
| Live in-game speed |
Speed + clarity |
Fast markets, stable bet slip, instant confirmation |
Lag, odds confusion, unclear bet status |
| Same-game combinations |
Control + strategy |
Transparent rules, easy review, easy tracking |
“Why can’t I combine?”, confusing payout math |
| Trust-first mainstream |
Reliability + payouts |
Predictable deposits/withdrawals, clear history, support |
Delayed payouts, unclear settlement, poor support |
The Final Takeaway
In 2026, successful sports betting app development demands more than feature completeness. It requires architecture-first thinking, compliance by design, and infrastructure engineered for real-time volatility. From real-time odds integration to embedded AML compliance and PCI compliance, every technical decision influences scalability, revenue stability, and regulatory continuity.
Operators seeking to build a sportsbook app must prioritize production-grade systems that withstand concurrency spikes and evolving regulatory landscapes.
If you are planning for a secure, scalable, and future-ready fantasy sports app development, partner with experts who understand high-performance betting ecosystems.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q. How to develop a betting app?
Ans. To develop a sports betting app, start with market research and licensing strategy, then design scalable architecture using microservices. Move to UI and UX design aligned with compliance and user flows. Integrate real-time odds feeds, secure wallet systems, AML compliance workflows, and PCI compliance–aligned payment infrastructure. Then proceed with backend engineering, testing, and compliance validation before launch.
Q. How much does it cost to develop a betting app?
Ans. The cost to develop a betting app in 2026 typically ranges from $20,000 to $40,000 for a basic MVP. A growth-ready platform with real-time odds integration and secure payments usually costs between $50,000 and $120,000, while complex or enterprise-grade sportsbooks can exceed $150,000 to $300,000+. Final costs depend on features, compliance requirements, integrations, and infrastructure complexity.
Q. Why is real-time odds integration critical in sports betting app development?
Ans. Real-time odds integration ensures live markets update instantly during matches. Sub-second latency prevents pricing errors, protects revenue, and improves in-play conversion rates. Without reliable event-driven pipelines and feed normalization, sportsbooks face financial exposure and settlement disputes.
Q. What compliance requirements must be embedded when developing a sportsbook app?
Ans. A sportsbook must embed AML compliance, KYC verification, PCI compliance for payments, geo-fencing enforcement, and audit-ready logging. These controls must be integrated at the architectural level to meet regulatory standards and prevent licensing risks.
Q. Should I choose white-label or custom sports betting app development?
Ans. White-label solutions reduce initial mobile app development cost and accelerate launch. Custom sports betting app development provides greater scalability, integration flexibility, compliance control, and long-term technical ownership. Growth-focused operators typically prefer custom architecture.
Q. How long does it take to develop a sports betting app?
Ans. A basic MVP may take 5–10 months. A growth-ready or custom sportsbook platform typically requires 8–12+ months, depending on feature complexity, real-time infrastructure, and compliance requirements.
Q. What technology stack is recommended for sports betting app development?
Ans. Modern sportsbooks use microservices architecture, event-driven systems, relational databases for transactions, NoSQL or in-memory caching for live data, and cloud-based auto-scaling infrastructure. Native or high-performance mobile frameworks are often combined with secure backend APIs to handle high concurrency.



 Facebook
Facebook
 Twitter
Twitter
 LinkedIn
LinkedIn
 Pinterest
Pinterest