Imagine your product team cutting idea to prototype time from months to weeks, without burning people out.
That shift is already happening.
Recent surveys show that about 78% of organizations now use AI in at least one business function, and adoption keeps climbing every quarter. Research on software product teams also shows that AI can reduce time to market by roughly 5% to 20% when applied across strategy, design, and engineering and model development.
This is why Generative AI in product development is moving from side experiment to core capability. Product leaders now use it across the full digital product lifecycle:
At Quokka Labs, we see a clear pattern. Teams that adopt generative AI with a structured plan move faster, make better decisions, and ship more user centric products.
This guide explains what this shift really means for modern product teams, where AI adds measurable value, and how to roll it out safely and responsibly.
What is Generative AI in Product Development?
Generative AI is a class of models that can make new content based on patterns in existing data. Instead of only classifying or predicting, they can:
-
Draft text and product documents
-
Propose interface layouts
-
Suggest data structures and APIs
-
Generate test cases and synthetic data
So, when we talk about Generative AI in product development, we mean using these models to support the work of product managers, designers, engineers, and QA teams across their daily tasks.
It is not magic. It is pattern recognition at scale, applied to real product workflows.
Why this shift matters
The move to Generative AI in product development matters because it changes basic constraints:
Teams can test more ideas in the same time window. AI helps generate options instead of starting from a blank page.
- Lower experimentation cost
You can explore alternative flows, copy, and designs without pulling a full team into each branch.
- Instant design and content alternatives
Instead of three versions from a designer or writer, you can review twenty and refine the best ones.
- Smarter insights from real time data
Models summarize feedback, research, and telemetry into patterns that humans can act on.
In short, AI compresses the distance between “what if” and “let’s try it.”
Core capabilities for product teams
We have seen a few core capabilities that repeat when teams adopt Generative AI in product development:
Text generation and transformation
-
Product requirement drafts
-
User stories, acceptance criteria, and release notes
-
Summaries of discovery calls and user interviews
Visual design and prototyping
-
Low fidelity UI ideas based on copy and flows
-
Layout suggestions that respect design systems
-
Variations for A B tests and localization
Workflow automation
-
Auto populate ticket fields and links
-
Generate PRD skeletons from backlog items
-
Convert high level ideas into structured tasks
Predictive and pattern-based insights
-
Group user feedback themes
-
Highlight risky areas in the roadmap
-
Predict defect hotspots earlier in the cycle
Used well, these blocks turn Generative AI in product development into a practical assistant, not a toy.
How Generative AI Accelerates Innovation Across the Product Lifecycle
Generative AI in product development during ideation
The first place AI helps is before any line of code is written.
Practical ideation support includes:
Turn problem statements, market gaps, or support data into structured idea lists.
- AI driven competitive analysis
Summarize competitor features, pricing, and positioning from public sources.
- Market insight extraction
Digest research reports, review sites, and survey answers into simple themes and signals.
- Prompt based brainstorming
Explore “what if” scenarios for new features, bundles, or pricing models.
- Structured concept generation
Take raw ideas and turn them into ready to discuss concepts with target users, jobs to be done, and value hypotheses.
This is one of the most common Generative AI use cases in product development because it reduces blank page fear and speeds up validation.
Generative AI for product design
When teams move into design, AI becomes a strong partner rather than a replacement. A focused use of Generative AI for product design can support:
- Rapid UI and UX concept creation
Turn flows and stories into screen level sketches in minutes.
- AI generated wireframes and layouts
Generate multiple layout versions that still respect base guidelines.
- Automated design variations
Create variants for different segments, markets, or accessibility needs.
- Early usability prediction
Use models to flag long flows, unclear labels, or heavy cognitive load before user testing.
- Real time design feedback
Get quick suggestions based on heuristics and past successful patterns.
Short table, traditional design versus AI enhanced design
| Aspect |
Traditional approach |
AI-enhanced approach |
| First wireframe set |
A few options over several days |
Dozens of options within hours |
| Design exploration |
Limited by team time |
Many more paths explored with low extra effort |
| Feedback cycles |
Mostly manual and meeting-based |
Continuous, with automated heuristics and quick design reviews |
| Experiment-ready UI |
Requires extra polish and copy work |
Draft copy and variants generated together with layouts |
Across industries, research now shows that applying Generative AI in product design and early prototyping shortens design cycles and reduces rework.
Generative AI in digital product development
Once your team moves deeper into build, Generative AI in digital product development helps the technical side of the lifecycle.
Common patterns include:
-
AI assisted user flows from business goals and personas
-
Faster API mockups and example payloads
-
Automated documentation stubs for endpoints and services
-
AI generated acceptance criteria aligned to user stories
-
PRD sections created from discovery notes and backlog grooming sessions
Here, Generative AI in product development acts like a bridge between product, design, and engineering. Everyone sees cleaner, more consistent artefacts.
Generative AI Use Cases in Product Development – Practical Breakdown
Across Quokka Labs clients, high ROI Generative AI use cases in product development tend to cluster around these areas:
- Automated requirements and PRDs
Turn raw notes, calls, and tickets into structured documents.
- Idea to prototype generation
Move from text description to simple clickable prototypes faster.
- Version control summaries
Summarize pull requests, changelogs, and branches into human friendly overviews.
- Feature prioritization support
Combine qualitative feedback and quantitative data to propose ranked lists.
- Voice of customer analysis
Cluster feedback from multiple sources and surface themes and sentiment.
Turn acceptance criteria into first draft test cases.
Flag features that touch sensitive flows, data, or infrastructure.
- Knowledge assistants for product teams
Provide fast answers from past decisions, documents, and experiments.
These use cases show why Generative AI in product development is no longer just a design topic. It touches everything.
AI in prototyping and engineering
Engineering teams feel pressure to ship faster without breaking stability. Here AI powered assistants make a direct difference.
Task level examples:
-
Auto generated code snippets from specs and comments
-
Code refactoring suggestions based on existing patterns
-
Test case automation for both unit and integration levels
-
Performance bottleneck detection from logs and traces
-
Simulation of user flows under different conditions
Task versus time saved snapshot
| Task |
Typical time before AI |
Time after AI support |
Comment |
| Drafting unit tests |
High |
Much lower |
AI suggests standard case patterns |
| Writing boilerplate API code |
High |
Lower |
Templates and snippets from models |
| Understanding old modules |
Medium |
Lower |
Summaries from code and docs |
| Drafting migration plans |
Medium |
Lower |
AI proposes steps from schema changes |
Studies on developer productivity confirm these patterns, with many teams reporting double digit productivity gains from AI assistance.

AI in testing and quality assurance
QA and test engineering often become bottlenecks. Generative AI supports them in several ways:
-
AI generated test scripts from requirements and user stories
-
Smart bug detection by spotting unusual patterns in logs and behavior
-
Pattern based defect prediction, highlighting modules that may fail based on history
-
Accurate test coverage estimation using code, tests, and risk models
-
Synthetic data creation to safely test edge cases and rare flows
This not only guards quality but also reduces repeat work late in the cycle.
AI in deployment, launch, and post launch optimization
The lifecycle does not end at release. Generative AI in product development continues after launch:
-
Auto created A B tests from copy and layout variants
-
Release note generation from merged pull requests
-
Feature rollout analytics with concise summaries
-
Demand forecasting based on past adoption and seasonality
-
Support documentation and FAQ automation from product changes
This is where teams close the loop and feed real world learning back into the next cycle.
Strategic Benefits of Using Generative AI In Product Development
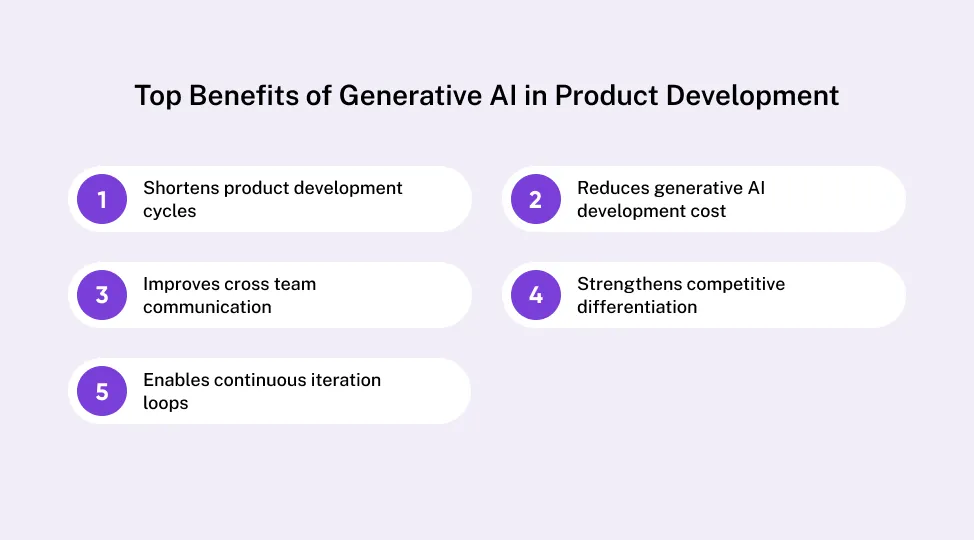
Shortens product development cycles
Key effects:
-
Fewer handoff delays between product, design, and engineering
-
Faster document, prototype, and test creation
-
Lower friction in decision making thanks to quick summaries
Over time, this means you can run more experiments per quarter with the same team size.
Reduces generative AI development cost
Well planned AI adoption reduces cost in two ways:
When you plan budgets, tools, and training, it helps to work with a clear view of generative AI development cost across models, infrastructure, and operations.
Improves cross team communication
Generative AI in product development smooths communication because:
-
Requirements are cleaner and more consistent
-
Decisions and trade offs are captured and summarized
-
Stakeholders get quick, tailored views of the same source information
Less time is wasted clarifying what work means.
Enhances decision making accuracy
Better decisions come from:
-
Data and feedback that is easier to digest
-
Simulations of scenarios and their likely impact
-
Early detection of risks and constraints
Teams can still use human judgement, but they do it with clearer context.
Strengthens competitive differentiation
With faster cycles and deeper insight, you can:
-
Reach product market fit sooner
-
Offer experiences that are harder to copy
-
Respond faster to moves from competitors
Generative AI in product development gives you extra “shots on goal” each year.
Enables continuous iteration loops
Because AI supports every stage, iteration becomes the default:
-
Learn from data and feedback
-
Generate improved ideas and designs
-
Implement and test faster
-
Measure and repeat
This loop is where long-term advantage is built.
Framework For Implementing Generative AI In Product Development

Discovery phase – understand your product needs
Start simple and specific:
-
Map ROI opportunities across the product lifecycle
-
Identify data sources available and their quality
-
Define model requirements in terms of inputs, outputs, and constraints
-
Pick two or three lighthouse use cases as pilots
This discovery work keeps you away from “AI for AI’s sake”.
Selecting the right models and tools
In practice, most teams mix:
-
Open-source AI models for flexibility and control
-
Foundation models from cloud providers for scale and reliability
-
Custom fine-tuned models for domain specific tasks
Your choice should consider data sensitivity, latency needs, and maintenance capacity.
Build Versus Buy – When to Use Partners
Many organizations mix internal efforts with external support, especially early on.
A specialized partner that offers generative AI development services can help you:
-
Validate use cases and feasibility
-
Design architecture and integration patterns
-
Set up infrastructure, observability, and governance
You still own the vision and roadmap. The partner helps you move faster and avoid early mistakes.
Creating A Generative AI Implementation Roadmap
A clear roadmap turns big ideas into manageable steps. A good Generative AI Implementation Strategy usually covers:
Step by step lifecycle plan
-
Ideation and prioritization of use cases
-
Data preparation and access control
-
Model selection, training, and evaluation
-
Integration into product tools and workflows
Security and compliance essentials
-
Data masking, anonymization, and retention rules
-
Access controls and audit logs
-
Policy and legal reviews for sensitive use cases
Model lifecycle management
-
Versioning, rollback, and promotion paths
-
Monitoring for drift, bias, and performance issues
-
Regular retraining and tuning cycles
This roadmap should be shared and understood by product, engineering, and leadership.
Executing A Real-World Generative AI Implementation
Once you have a strategy, the work moves into execution. A practical Generative AI implementation usually follows these phases:
1. Data collection and preparation
-
Gather relevant product, usage, and feedback data
-
Clean, label, and structure it for training and evaluation
2. Model training and refinement
3. Integration with product tools
-
Connect models to design, planning, and engineering tools
-
Build simple, clear interfaces for end users
4. UX and workflow alignment
5. Evaluation and testing
-
Measure quality, latency, and reliability
-
Include human review for high risk actions
6. Deployment and ongoing monitoring
-
Roll out in stages, starting with small groups
-
Track usage patterns, failures, and impact metrics
This structure lets you scale Generative AI in product development without losing control.
Cost Of Adopting Generative AI In Product Development
Budget planning is critical. Here is a simple cost view.
| Cost component |
What it covers |
Notes |
| Model training |
Compute, data preparation, labelling |
Highly dependent on scale |
| Fine-tuning |
Domain-specific model refinement |
Great for niche use cases |
| Integration |
Engineering work to connect systems |
Often a one-time effort |
| Deployment |
Cloud or on-prem infrastructure |
Ongoing operational expense |
| Monitoring and maintenance |
Logging, evaluation, updates, QA |
Monthly or quarterly cycles |
For startups, cost focus is usually on:
-
existing foundation models
-
Keeping infrastructure simple and cloud based
-
Targeting one or two high impact use cases first
For enterprises, cost drivers include:
-
Stronger compliance and security needs
-
Integration with legacy systems
-
Broader scope across many products and teams
In both cases, understanding your true generative AI development cost early makes it easier to set realistic ROI targets.
Challenges, Risks, And How to Avoid Them
Data quality limitations
Poor data leads to weak outcomes.
Mitigation:
-
Delay automation until you have enough clean data
-
Start with narrow tasks where you trust the inputs
-
Invest in better data pipelines as part of the project
Over dependence on AI output
Teams may start accepting model suggestions without enough thought.
Mitigation:
-
Keep humans in the loop for key decisions
-
Train teams to treat AI as a draft, not a verdict
-
Use clear labels and confidence indicators in tools
Privacy and compliance issues
Generative AI in product development often touches sensitive user and business data.
Mitigation:
Apply strict data minimization, masking, and anonymization
Keep sensitive training and inference inside secure boundaries
Involve legal and compliance early in the roadmap
Misalignment with product goals
There is a risk of chasing impressive demos instead of solving core problems.
Mitigation:
-
Tie each use case to clear product metrics
-
Review AI projects in the same forums as other product work
-
Kill pilots that do not show practical value
Hidden model maintenance complexity
Models drift and degrade over time.
Mitigation:
-
Treat models like long lived services, not one off projects
-
Plan for regular evaluation and retraining
-
Document assumptions and limitations for each use case
Risk versus mitigation snapshot
| Risk |
Mitigation focus |
| Low quality or biased data |
Data governance and curation |
| Blind trust in outputs |
Human review and training |
| Privacy breaches |
Strong security and legal oversight |
| Misaligned roadmap |
Metric-based prioritization |
| Rising maintenance overhead |
Clear ownership and lifecycle management |
Examples and Case Studies – Generative AI In Product Development Done Right
These sample scenarios mirror real outcomes we see across the market.
- SaaS product speeding up design cycles
A B2B SaaS team uses Generative AI in product development to create early UI concepts and copy drafts. Designers now spend more time on refinement and user research. Result: around 30 percent faster concept to test cycle and more A B tests per quarter.
- Ecommerce brand using AI for personalization concepts
A retail brand applies Generative AI in digital product development to generate personalised offer ideas, landing pages, and email content based on segments. Result: faster creative turnaround and higher engagement metrics on experiments.
- B2B platform accelerating backlog creation
A platform team feeds discovery notes and call summaries into an AI assistant that creates structured epics, user stories, and acceptance criteria. Result: product managers reclaim several hours a week, and engineering gets clearer inputs.
- Fintech enhancing risk analysis with AI
A fintech company uses Generative AI use cases in product development to summarize regulatory changes and flag product features that may need extra review. Result: fewer last minute compliance surprises and smoother releases.
These examples show that success is not about giant one off projects. It comes from steady, practical application.
Future Trends Shaping Generative AI In Product Development
Looking ahead, we see several trends that will shape how teams use Generative AI in product development:
-
Multimodal design copilots that combine text, visuals, and data into shared workspaces
-
Real time prototyping where teams edit flows in natural language and see screens update live
-
AI scenario testing that simulates user behavior across segments and channels
-
Autonomous road mapping helpers that suggest priorities based on data and strategy inputs
-
Full tooling chain AI integration across design systems, issue trackers, and CI CD pipelines
-
Engineering and design agents that collaborate to resolve issues and propose improvements
-
AI led UX optimization that continuously suggests layout and copy tweaks based on real usage
These trends will make AI feel less like a separate tool and more like part of the product fabric.
Conclusion – AI Becomes a Core Driver of Product Innovation
Generative AI in product development is no longer optional for teams that want to move fast and stay relevant.
Used well, it accelerates every stage of the lifecycle:
The real advantage does not come from one big model. It comes from many small, well-chosen use cases, rolled out with care, measured with clear metrics, and improved over time.
At Quokka Labs, we believe the next wave of standout digital products will come from teams that treat Generative AI as a practical partner, not a headline. If you are ready to turn ideas into working, AI powered product workflows, this is the right moment to start.




 Facebook
Facebook
 Twitter
Twitter
 LinkedIn
LinkedIn
 Pinterest
Pinterest