Customer expectations have shifted toward transparency, convenience, instant fulfillment, and real-time visibility. Whether booking a ride, ordering food, or scheduling a home service, users expect immediate confirmation, live status updates, and predictable fulfillment.
This shift has made on-demand application development a strategic priority for businesses where speed, coordination, and service reliability directly impact customer retention, driving growing demand for robust mobile app development services that can support real-time operations at scale. An on-demand platform is not simply a transactional interface. It functions as a real-time coordination layer that synchronizes users, service providers, payments, and operational workflows.
This makes on-demand service app development inherently complex, involving location intelligence, live availability, secure payments, and continuous data flow across multiple systems.
What is an On-Demand Application?
An on-demand application is a digital platform designed to deliver services or products instantly by connecting users with service providers in real time. Unlike traditional applications that rely on scheduled interactions or delayed fulfillment, on-demand platforms are built around immediacy, availability, and continuous coordination between multiple parties.
At its core, on-demand iOS or Android app development focuses on creating systems that can match demand with supply dynamically. This includes handling real-time requests, managing provider availability, processing secure payments, and offering live status updates throughout the service lifecycle. The success of an on-demand platform depends not only on user experience but also on the reliability and scalability of the underlying infrastructure.
From a business perspective, an on-demand application operates as a marketplace, an operations engine, and a customer experience platform combined. This is what differentiates on-demand software development from conventional app development approaches.
Core Definition and Characteristics
An on-demand application is typically defined by a few foundational characteristics that enable real-time service delivery at scale. These characteristics shape every aspect of on-demand app development, from architecture decisions to feature prioritization.
Key characteristics include:
-
Real-time matching between users and service providers based on availability, location, and predefined business rules.
-
Location intelligence using GPS and mapping services to enable tracking, routing, and navigation.
-
Instant booking and fulfillment, minimizing wait times and friction.
-
Secure digital payments with automated transaction handling.
-
Feedback loops through ratings and reviews to maintain service quality.
Unlike standard Android or iOS app development or web applications, an on-demand platform must operate continuously under variable demand conditions.
This requires backend systems that can process concurrent requests, synchronize data across apps, and maintain performance during peak usage, supported by scalable backend development services designed for high-traffic, real-time environments. As a result, on-demand application development prioritizes reliability and responsiveness over static feature sets.
How On-Demand Applications Work End-to-End
Understanding the end-to-end flow of an on-demand application helps clarify why architecture plays such a critical role in on-demand service app development.
A typical workflow includes:
-
User request initiation: The user selects a service, defines requirements, and places a request through the user app.
-
Provider discovery and availability check: The system evaluates nearby providers based on location, availability, and predefined matching rules.
-
Real-time matching and confirmation: A suitable provider accepts the request, and the service is confirmed instantly.
-
Service execution and live tracking: Both users and providers receive real-time updates, including location tracking and status notifications.
-
Payment processing and settlement: Payments are processed securely, with commissions or fees automatically applied.
-
Feedback and data capture: Ratings, reviews, and operational data are stored to improve future matching and service quality.
This continuous data exchange across user apps, provider apps, and backend systems is what makes on-demand application development fundamentally different from traditional application workflows. Each interaction must be reliable, fast, and scalable to support consistent user experiences as demand grows.
On-Demand Application Architecture: How These Platforms Are Built
A scalable on-demand application is defined less by its interface and more by the architecture that supports real-time operations. On-demand platforms must process continuous requests, manage live provider availability, handle payments securely, and maintain system stability during traffic spikes. This makes architecture a foundational decision in on-demand application development, not an afterthought.
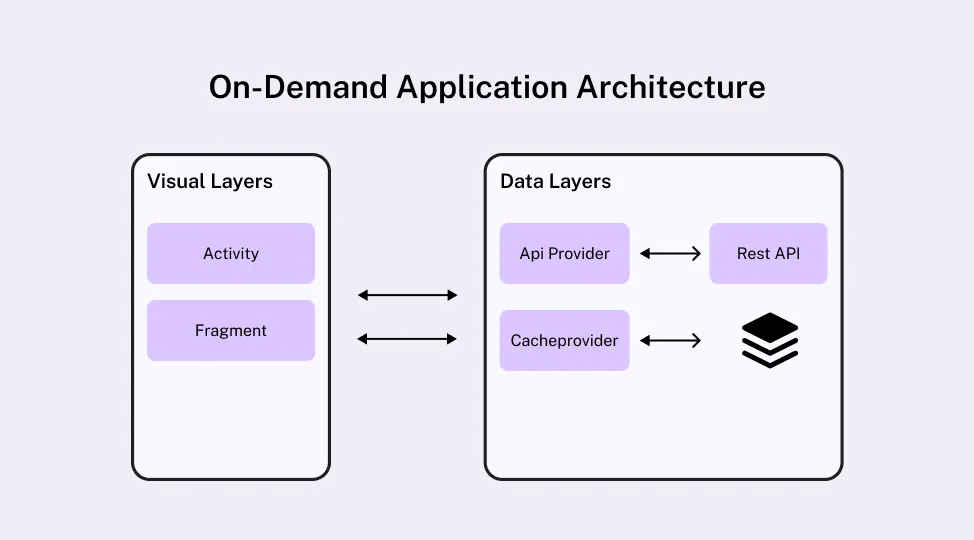
Successful on-demand platforms are typically designed as distributed systems, often using service-oriented or microservices architectures to support scale. The goal is to ensure low latency, high availability, and consistent performance as the platform scales across users, providers, and regions.
Three-Tier Architecture of an On-Demand Application
Most on-demand platforms follow a three-tier architecture that separates responsibilities across different applications. This structure is central to reliable on-demand service app development.
The three tiers include:
-
User App: Designed for customers to search for services, place requests, track fulfillment, and make payments. The user app focuses on speed, simplicity, and transparency.
-
Provider App: Used by service providers to manage availability, accept or reject requests, navigate to service locations, and track earnings. Provider apps must be optimized for real-time updates and operational efficiency.
-
Admin Panel: Acts as the control center for the platform. It enables business teams to manage users and providers, monitor transactions, configure pricing, resolve disputes, and analyze platform performance.
Separating these layers allows businesses to scale each component independently. As demand increases, on-demand application development benefits from this modular approach by reducing system bottlenecks and improving maintainability.
Backend Architecture for On-Demand App Development
The backend is the backbone of any on-demand application, responsible for coordinating real-time interactions across all platform components. A robust backend architecture ensures that requests are processed reliably, even under high concurrency.
Key backend components include:
-
Application servers that handle business logic and service orchestration.
-
Databases for storing user profiles, provider data, transactions, and operational logs.
-
APIs that enable communication between user apps, provider apps, and external services.
-
Real-time engines that support live updates, notifications, and tracking.
In modern on-demand software development, backend systems are often designed using a microservices approach. This allows individual services such as payments, matching, notifications, and analytics to scale independently. The result is improved fault isolation and better performance during peak usage.
Key Technologies Powering On-Demand Software Development
Technology choices directly impact the reliability and scalability of an on-demand platform. Selecting the right tools is a critical step in on-demand application development.
Common technologies include:
-
GPS and geolocation services for real-time tracking and proximity-based matching.
-
Push notifications and real-time messaging to keep users and providers informed.
-
Payment gateways to handle secure and compliant transactions.
-
Cloud infrastructure with seamless cloud integration to support elastic scaling and high availability.
-
Analytics systems to monitor performance, demand patterns, and user behavior.
Together, these technologies enable on-demand platforms to operate continuously while adapting to fluctuating demand. This technology stack forms the operational foundation of effective on-demand service app development.
Security, Compliance, and Data Management
Security and compliance are critical considerations in on-demand application development, especially when handling payments, personal data, and location information. Because on-demand platforms handle payments, identity data, and real-time location information, security failures directly impact trust and regulatory exposure.
Key mobile app security measures include:
-
Encrypted data transmission and storage.
-
Secure authentication and role-based access control.
-
Fraud detection and payment security mechanisms.
-
Compliance with industry and regional data regulations.
Strong data management practices ensure platform stability and long-term trust. As on-demand platforms scale, consistent governance of user, provider, and transaction data becomes essential for both operational efficiency and regulatory readiness.
Common Use Cases of On-Demand Application Development Across Industries
The flexibility of an on-demand application has enabled businesses across multiple industries to deliver services with greater speed, transparency, and operational control. While the core architecture remains similar, each industry applies on-demand application development differently based on customer expectations, regulatory requirements, and fulfillment complexity.
Understanding these use cases helps businesses evaluate how on-demand models can be adapted to their specific market needs.
1. Transportation and Mobility Platforms
Transportation was one of the earliest adopters of the on-demand model. Ride-hailing and mobility platforms rely heavily on real-time coordination between users and drivers.
Key characteristics include:
-
Instant ride requests and dynamic driver matching.
-
GPS-based navigation and live tracking.
-
Demand-based pricing adjustments during peak hours.
-
High concurrency during traffic surges and events.
In this sector, on-demand app development must prioritize low latency and system resilience. Even minor delays in matching or tracking can impact user trust and platform reliability.
2. Food, Grocery, and Hyperlocal Delivery
Food and grocery delivery platforms operate under tight fulfillment timelines and fluctuating demand. These platforms often involve multiple stakeholders, including vendors, delivery partners, and end users.
Key considerations include:
-
Real-time order processing and status updates.
-
Integration with vendor systems and inventory management.
-
Route optimization for faster deliveries.
-
Handling peak demand during meal times and promotions.
Effective on-demand application development in this space requires strong backend orchestration to manage simultaneous orders without service degradation.
💡Suggested Read: How Much Does Food Delivery App Development Cost?
3. Home Services and Local Service Marketplaces
Home services platforms connect users with professionals for cleaning, repairs, beauty services, and maintenance. Trust, quality, and availability play a central role in user adoption.
Core platform requirements include:
-
Service discovery based on location and skill sets.
-
Provider verification and onboarding workflows.
-
Scheduling flexibility and instant booking options.
-
Ratings and reviews to maintain service standards.
For this category, on-demand service app development must balance speed with service quality, ensuring reliable matching and consistent customer experiences.
4. Healthcare and On-Demand Medical Services
Healthcare on-demand platforms address the growing need for accessible medical services, including consultations, diagnostics, and medicine delivery.
Typical use cases involve:
-
Appointment booking and virtual consultations.
-
Secure handling of sensitive health data.
-
Integration with pharmacies and logistics providers.
-
Compliance with healthcare regulations.
Because of regulatory and data sensitivity, on-demand software development in healthcare places strong emphasis on security, compliance, and auditability.
💡Suggested Read: Build a HIPAA-Compliant Healthcare App
5. Logistics and Enterprise On-Demand Platforms
Logistics and courier services use on-demand models to optimize last-mile delivery and enterprise workflows.
Key features include:
-
Real-time shipment tracking and status updates.
-
Fleet management and route optimization.
-
SLA monitoring and performance analytics.
-
Integration with enterprise systems.
In this context, on-demand application development supports both customer-facing experiences and internal operational efficiency, making scalability and reliability critical success factors.

Business Models Behind Successful On-Demand Applications
A well-designed on-demand application is only sustainable when supported by a clear and scalable revenue strategy. While technology enables real-time service delivery, business models determine how value is captured from each transaction.
Selecting the right monetization approach is a critical part of on-demand application development, as it directly impacts unit economics, provider participation, and long-term growth.
Most on-demand platforms rely on a combination of business models rather than a single revenue stream. This layered approach allows platforms to adapt pricing strategies as the marketplace matures.
1. Commission-Based Model
The commission-based model is the most widely used approach in on-demand app development. Platforms charge a percentage fee for every successful transaction completed through the application.
This model works well when:
-
Transaction volumes are high.
-
Services are standardized.
-
The platform adds clear value through discovery and fulfillment.
Commission-based monetization aligns platform revenue with service usage, making it a scalable option for many on-demand businesses. However, commissions must be carefully structured to maintain provider engagement and competitive pricing.
2. Subscription-Based Access
Subscription models generate recurring revenue by charging users or service providers a fixed fee for access to premium features or increased visibility.
Common subscription use cases include:
-
Monthly provider memberships for higher lead volume.
-
User subscriptions for reduced service fees or faster fulfillment.
-
Enterprise access plans for business clients.
In on-demand application development, subscriptions help stabilize revenue and reduce dependence on transaction volume alone. This model is often introduced as platforms reach operational maturity.
3. Surge Pricing and Dynamic Pricing Models
Dynamic pricing adjusts service costs based on real-time demand and supply conditions. This model is commonly used in transportation, delivery, and logistics platforms.
Key advantages include:
-
Better demand-supply balance during peak hours.
-
Incentives for providers to remain available.
-
Improved service availability under high demand.
While effective, surge pricing requires transparency and user education. In on-demand software development, pricing algorithms must be carefully implemented to avoid negative customer experiences.
4. Freemium and Value-Added Services
Freemium models offer basic functionality at no cost while charging for advanced features or enhanced services.
Examples include:
This approach lowers entry barriers for users while creating upsell opportunities. In on-demand service app development, freemium models work best when premium features clearly enhance operational or customer outcomes.
5. Advertising and Featured Listings
Advertising-based monetization allows service providers to pay for increased visibility within the platform.
Common implementations include:
-
Featured service listings
-
Sponsored placements in search results
-
Promotional campaigns during high-demand periods
This model is most effective once the platform reaches scale and has sufficient user traffic. It is often used as a supplementary revenue stream in mature on-demand application ecosystems.
Key Features Required for On-Demand Service App Development
The success of an on-demand application depends on how effectively it supports real-time interactions between users, service providers, and platform operators. Feature design in on-demand service app development must balance simplicity for end users with operational control and scalability for businesses, making UI UX design a critical factor in reducing friction and improving adoption.

Each component of the platform plays a distinct role in delivering a seamless on-demand experience.
1. User-Side Features
The user-facing application is the primary entry point for service requests. In on-demand application development, user features are designed to reduce friction and provide continuous visibility throughout the service lifecycle.
Essential user-side features include:
-
Service discovery and search based on location, availability, and preferences.
-
Instant booking and scheduling options.
-
Real-time tracking of service progress or delivery status.
-
Secure payment processing with multiple payment methods.
-
Ratings and reviews to build trust and accountability.
These features directly influence user retention and satisfaction. A consistent and responsive user experience is critical for long-term adoption of any on-demand application.
2. Provider-Side Features
The provider app enables service professionals to manage requests efficiently while maintaining flexibility and control over their availability.
Key provider-side features include:
-
Availability management and status updates.
-
Request acceptance and task management.
-
Navigation and route optimization.
-
Earnings and payout tracking.
-
Performance insights through basic analytics.
In on-demand app development, provider experience is just as important as user experience. Well-designed provider features help maintain service quality and reduce churn within the supply network.
3. Admin Panel Capabilities
The admin panel acts as the operational backbone of the on-demand platform. It provides visibility and control over the entire ecosystem.
Core admin features include:
-
User and provider management.
-
Pricing, commission, and promotion configuration.
-
Payment monitoring and settlement management.
-
Dispute resolution and support workflows.
-
Analytics and reporting dashboards.
Strong admin capabilities enable businesses to optimize performance, identify bottlenecks, and make data-driven decisions. In scalable on-demand application development, the admin panel plays a central role in maintaining platform stability and governance.
Strategic Considerations Before Starting On-Demand App Development
Building an on-demand application requires more than technical execution. Strategic planning plays a critical role in determining whether the platform can scale sustainably while maintaining service quality. Before initiating on-demand application development, businesses must evaluate operational, market, and technical factors that influence long-term success.
These considerations help align product decisions with real-world demand and business objectives.
1. Market Readiness and Demand Validation
The viability of an on-demand platform depends on consistent demand and an active supply network. Before investing in on-demand app development, it is essential to validate:
-
User demand frequency and urgency
-
Service availability within target locations
-
Competitive saturation and differentiation opportunities
Without sufficient market readiness, even a well-built on-demand application may struggle to achieve traction.
2. Supply-Side Onboarding and Retention
On-demand platforms are only as strong as their provider network. Effective on-demand service app development must account for:
-
Provider onboarding workflows.
-
Verification and compliance requirements.
-
Incentives that encourage long-term participation.
Balancing supply growth with user demand helps maintain service reliability and consistent fulfillment rates.
3. Unit Economics and Cost Structure
Understanding unit economics is essential for sustainable on-demand software development. Businesses should assess:
-
Customer acquisition costs
-
Provider incentives and payouts
-
Platform commissions and margins
-
Infrastructure and operational expenses
Clear visibility into unit economics allows platforms to refine pricing strategies and scale profitably.
4. Scalability and Performance Planning
On-demand platforms experience unpredictable demand spikes. Scalability must be built into the architecture from the start.
Key planning areas include:
-
Load handling during peak usage
-
Database performance under high concurrency
-
Geographic expansion readiness
Proactive scalability planning reduces operational risk as the on-demand application grows.
- MVP Scope and Feature Prioritization
Launching with a focused MVP helps validate assumptions without over-investing. In on-demand application development, MVPs typically focus on:
As usage patterns emerge, features can be expanded strategically based on real-world data.
Final Takeaway
An on-demand application succeeds when technology, operations, and business strategy work in alignment. While instant service delivery is the core promise, long-term success depends on building platforms that can handle real-time demand, scale reliably, and maintain sustainable unit economics. This makes on-demand application development a strategic investment rather than a purely technical initiative.
From defining the right architecture and identifying high-impact use cases to selecting monetization models that support growth, every decision influences platform performance and customer experience. Businesses that approach on-demand software development with a clear roadmap are better positioned to adapt to changing market dynamics and user expectations.

Frequently Asked Questions About On-Demand Application Development
1. How long does on-demand application development typically take?
The timeline for on-demand application development depends on platform complexity, integrations, and feature scope.
A focused MVP with core booking, matching, payments, and admin controls typically takes 12–20 weeks.
More advanced platforms involving multi-city scaling, enterprise integrations, real-time analytics, and complex pricing engines may require 6–9 months.
The key factor is not just feature count, but architectural decisions that determine scalability and long-term maintainability.
2. What is the average cost of on-demand app development?
The cost of on-demand app development varies based on scope, technology stack, compliance requirements, and scalability expectations.
Typical investment ranges:
- MVP-level on-demand application development: $40,000 – $80,000
- Mid-scale production platform: $80,000 – $150,000
- Enterprise-grade on-demand software development: $150,000+
Cost is largely influenced by backend complexity, real-time systems, cloud infrastructure, and integration requirements.
3. What technology stack is best for on-demand software development?
There is no universal stack, but scalable on-demand software development typically includes:
- Cloud-native backend architecture
- Microservices or modular service-oriented design
- Real-time communication engines
- Secure payment gateway integrations
- GPS and geolocation services
- Relational + caching databases for high concurrency
Technology decisions should prioritize scalability, low latency, and fault isolation rather than short-term development convenience.
4. How do you ensure scalability in on-demand application development?
Scalability is built into architecture, not added later.
In on-demand service app development, scalability requires:
- Load-balanced application servers
- Distributed databases
- Independent scaling of matching, payment, and notification services
- Queue systems for high request volumes
- Cloud auto-scaling capabilities
Without architectural planning, traffic spikes can create cascading failures across matching, payments, and tracking systems.
5. What are the biggest technical challenges in on-demand app development?
Common challenges include:
- Real-time demand-supply matching under high concurrency
- Maintaining low latency during peak traffic
- Payment reconciliation and settlement automation
- Provider retention and availability management
- Handling geographic expansion without degrading performance
Successful on-demand application development requires strong backend orchestration and operational analytics to prevent bottlenecks.
6. How do on-demand platforms maintain data security and compliance?
On-demand platforms handle payments, identity information, and often location data. Security cannot be an afterthought.
Effective on-demand software development includes:
- End-to-end encryption
- Secure authentication and role-based access
- Fraud detection mechanisms
- Regulatory compliance with regional data laws
- Audit logging and monitoring systems
Security architecture must scale alongside platform growth.
7. Should you build a custom on-demand application or use a ready-made solution?
Ready-made solutions can help test early ideas quickly, but they limit flexibility in pricing models, integrations, and scalability.
Custom on-demand application development is recommended when:
- You require differentiated workflows
- You need enterprise integrations
- You plan multi-region expansion
- Unit economics require optimized cost control
Long-term competitive advantage usually requires ownership of architecture and data.
8. How do you choose the right development partner for on-demand application development?
When evaluating a development partner, look for:
- Experience with real-time systems
- Architecture-first approach
- Understanding of marketplace business models
- Ability to plan unit economics and scalability
- Proven deployment of production-ready on-demand platforms
On-demand service app development is not just mobile development. It is systems engineering, operations design, and business modeling combined.
Tags
Application Architecture
custom app development
ai implementation
App Security
App Development



 Facebook
Facebook
 Twitter
Twitter
 LinkedIn
LinkedIn
 Pinterest
Pinterest